Figure 2. Calculation of the Normalized Inhibitory Quotient (NIQ).
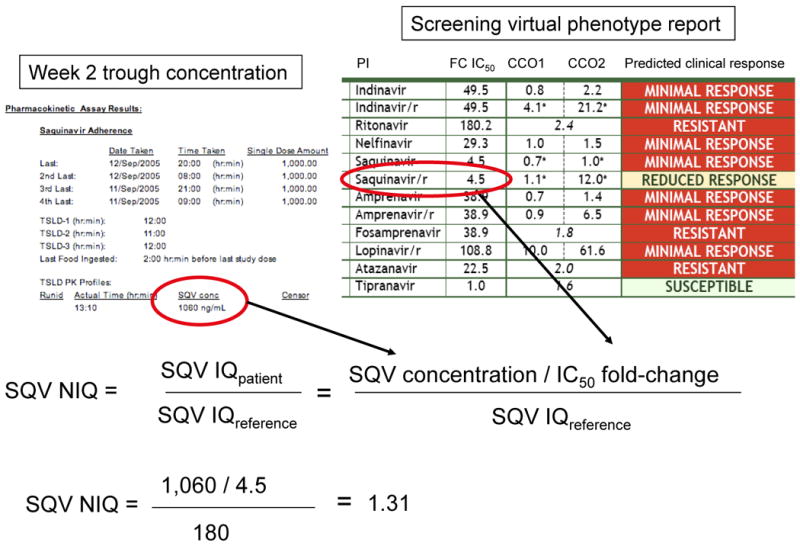
The method for calculating an NIQ is illustrated. The NIQ is the ratio of the patient's IQ to a reference IQ, which was obtained from a population of patients that was expected to achieve virologic success (180 in this example). The patient's IQ is the ratio of the week 2 plasma trough concentration of the PI being taken (in this case, saquinavir) and the fold-change in IC50 for the same PI obtained at the screening visit. In this example, the NIQ is greater than one, and the study patient would either enter the Observational arm, or discontinue the study. SQV, saquinavir; FC IC50, fold-change in the 50% inhibitory quotient for the patient's virus; CCO1, 1st clinical cutoff (threshold below which one would expect maximal virologic response); CCO2, 2nd clinical cutoff (threshold above which one would expect little or no virologic response). If the fold-change in IC50 is between CCO1 and CCO2, a reduced, but detectable virologic response would be expected). For protease inhibitors that have only a single cutoff (such as atazanavir and tipranavir in this specific example), this represents a biological cutoff for resistance, rather than a clinical cutoff.
