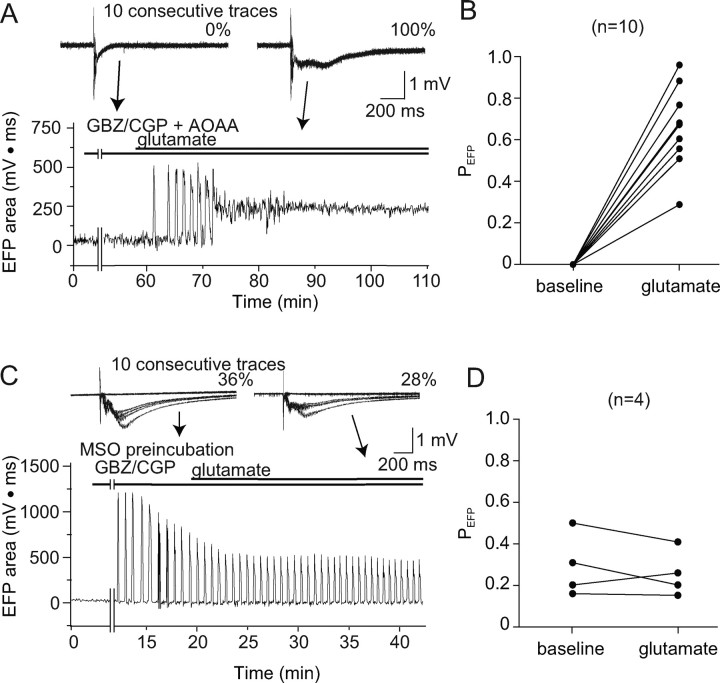
Figure 8.
Glutamate rescues EFP responses in AOAA- but not MSO-treated slices. A, Sample traces (top) and time course of evoked field potential area (bottom) from recordings of a cortical slice treated with AOAA and GBZ/CGP demonstrates that the initial absence of large evoked epileptiform field potentials is reversed by the addition of 250 μm glutamate to the perfusate. Numbers near tracings indicate the percentage of stimuli that evoked an epileptiform field potential. B, Paired analysis of PEFP before and 15 min after addition indicates a consistent increase with glutamate (n = 10; p < 0.0001). C, In contrast, sample traces (top) and time course of evoked field potential area (bottom) from recordings of a cortical slice treated with MSO and GBZ/CGP show no consistent change with addition of 250 μm glutamate. Numbers near tracings again indicate the percentage of stimuli that evoked EFPs. D, Paired analysis of PEFP at baseline (10 min after the addition of GBZ/CGP) and 15 min after addition of glutamate demonstrates a failure of glutamate to rescue EFPs in MSO-treated slices (n = 4; p = 0.40).