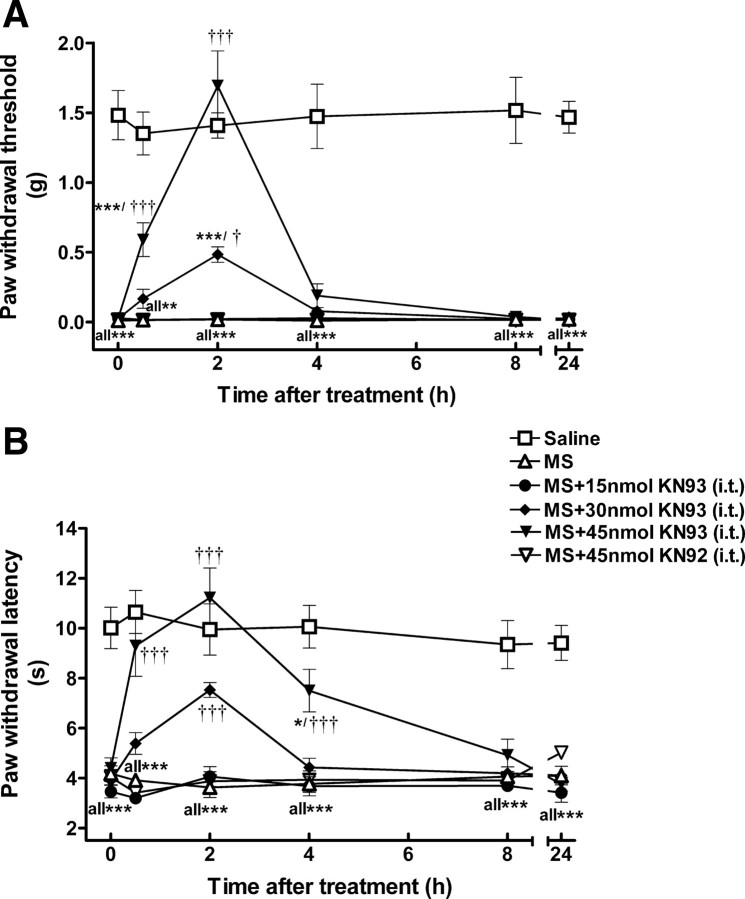
Figure 3.
Reversal of morphine-induced mechanical allodynia (A) and thermal hyperalgesia (B) by KN93. OIH was induced by intermittent morphine injections. On day 5, mice received KN93 (15–45 nmol, i.t.), KN92 (45 nmol, i.t.), or saline (intrathecally) at time 0. Mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia were tested at the different time points as indicated. KN93, but not KN92, reversed the established morphine-induced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, compared with the saline-treated group; †p < 0.05, †††p < 0.001, compared with the morphine-treated group; n = 8 for each group.