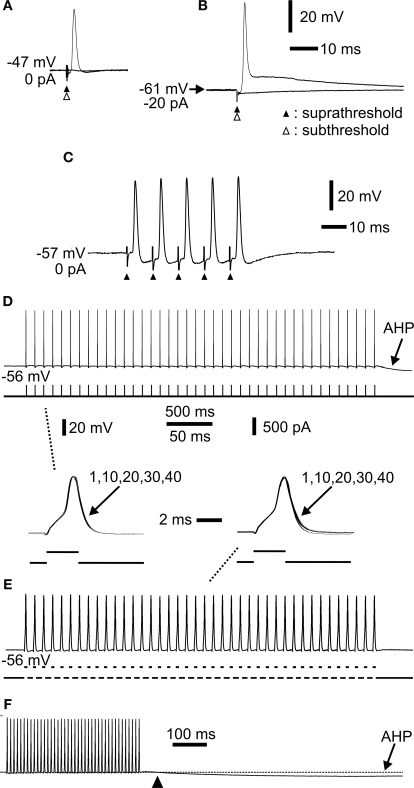
Figure 3.
Extracellular stimulation and repetitive spiking of mossy fibres. (A) Extracellular sub- (open arrowhead) and suprathreshold (closed arrowhead) stimulation showing all-or-none spike. (B) Hyperpolarization by constant current injection through the electrode shows a robust spike. Lowering the extracellular stimulus intensity (open arrow head) shows the all-or-none nature of the spike. (C) Repetitive activation at 100 Hz. The spikes readily followed the stimulation. Each stimulus is indicated by an arrowhead. (D) Repetitive activation at 10 Hz by a train of short current pulses injected intra-axonally through the recording electrode. Note afterhyperpolarization (AHP) following cessation of activation. Inset below to the left (indicated by dashed line) shows spike 1, 10, 20, 30 and 40 superimposed. No change in spike amplitude or duration was observed. (E) Repetitive activation at 100 Hz by a train of short current pulses injected intra-axonally. Inset above to the right (indicated by dashed line) shows spike 1, 10, 20, 30 and 40 superimposed. (F) The same sweep as in (E) at a slower sweep speed where the AHP had time to develop (arrowhead indicates start of AHP). Same voltage and current calibrations in (D), (E), (F) and insets between (D) and (E). Separate time calibrations are indicated between insets, and in (F), respectively. (A), (B), (C), and (D–F) from three different axons.