Figure 4.
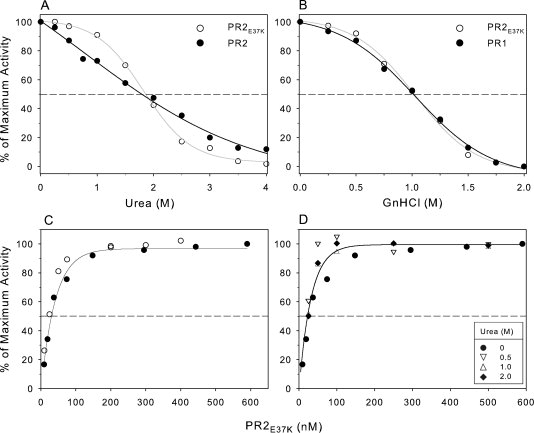
(A and B) Effect of urea and guanidine hydrochloride on catalytic activity. Catalytic activity was measured by monitoring the hydrolysis of substrate IV by 120 nM PR2 and 150 nM PR2E37K in 50 mM sodium acetate buffer, pH 5, at 28°C. For complete experimental details, see text. (A) Comparison of the catalytic activities of PR2E37K and PR2 as a function of increasing urea concentration. (B) Comparison of the catalytic activities of PR2E37K and PR1 as a function of increasing GnHCl concentration. (C) Effect of enzyme concentration on the activity of PR2E37K in 50 mM acetate buffer, pH 5, containing 250 mM NaCl, at 28°C, in the absence of urea. Solid and open circles are data from two separate experiments. (D) Lack of an effect of urea on the concentration dependence of PR2E37K activity: solid circles, no urea [data from (C)]; inverse triangles, 0.5M urea; triangles, 1.0M urea; solid diamonds, 2M urea. Note that each data set was normalized to a maximum activity of 100%. The lower urea concentrations had little effect on the maximum activity, but in the presence of 2M urea, the observed maximum activity was ∼60% of that in the absence of urea.
