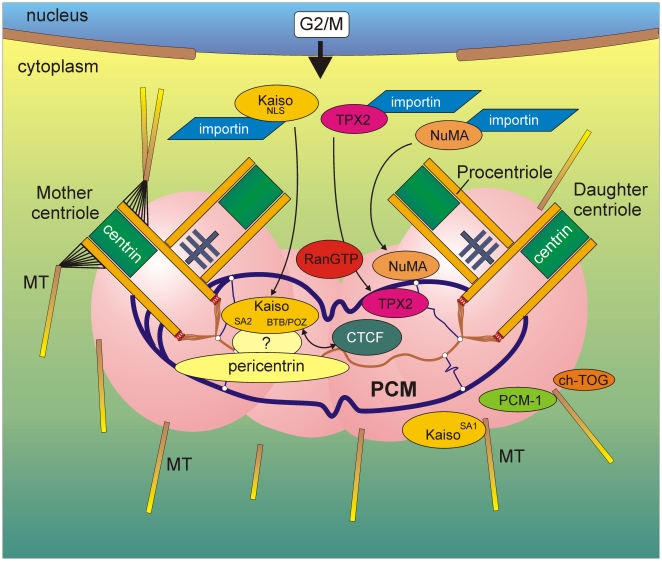
Figure 13. Hypothetical model for interactions of Kaiso's functional domains at the centrosomes during the onset of mitosis.
The Kaiso domains putatively responsible for its localization at the centrosomes or spindle microtubules are shown inside yellow Kaiso balloons. At the G2/M phase, the centrosome consists of a mother and a daughter centriole [drawn according to 44], as well as two growing procentrioles. Centrin (depicted in green) is concentrated in the centriolar distal lumen. MT, microtubules.A role for the SA2 domain of Kaiso: After breakdown of the nuclear envelope, nuclear proteins, such as NuMA, TPX2 and possibly also Kaiso, are released in a RanGTP-dependent manner from complexes containing importin. A fraction of RanGTP is present at the centrosomes throughout the cell cycle and can locally activate these centrosomal factors during G2/M phase; this allows microtubule nucleation and stabilization near the centriole pairs [69]. The molecular Kaiso-pericentrin interaction in the PCM, which is direct or indirect via an adaptor (depicted as ?), might also be a function of the SA2 domain.A role for the SA1 domain: Kaiso might associate either directly with the microtubules or indirectly via the motor protein dynein, along with other centrosomal components such as PCM-1 and ch-TOG.A role for the BTB/POZ domain in the centrosome: The zinc finger protein CTCF might recruit Kaiso towards the centrosomes (or vice versa) via the hetero-dimerization capacities of Kaiso's BTB/POZ domain.