Table 2.
L-Proline-Catalyzed Aldol Reaction of Racemic α-Ketophosphinates and Acetonea
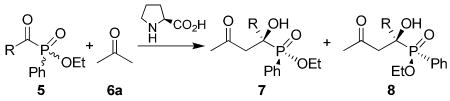 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | R | T (°C) | time (h) | yield (%)b | ee (%)c | drd | |
| 7 | 8 | ||||||
| 1 | Ph(a) | -30 | 96 | 58 | 99 | 91 | 52:48 |
| 2 | 4-F-C6H4(b) | -30 | 120 | 67 | 98 | 91 | 50:50 |
| 3 | 3-FC6H4(c) | 0 | 36 | 89 | 96 | 80 | 52:48 |
| 4 | 4-BrC6H4(d) | -30 | 120 | 70 | 97 | 87 | 54:46 |
| 5 | 4-ClC6H4(e) | -30 | 120 | 65 | 94 | 73 | 52:48 |
| 6 | 3-ClC6H4(f) | 0 | 36 | 92 | 99 | 89 | 53:47 |
| 7 | 4-MeC6H4(g) | -30 | 120 | 45 | 90 | 80 | 54:46 |
| 8 | 4-MeOC6H4(h) | rt | 40 | 87 | 93 | 71 | 56:44 |
| 9 | rt | 48 | 85 | 84 | 62 | 46:54 | |
| 10 | Me(j) | rt | 24 | 88 | 95 | 87 | 44:56 |
| 11 | Et(k) | rt | 40 | 90 | 87 | 61 | 45:55 |
Unless otherwise indicated, all reactions were carried out with the racemic ketophosphinate (0.50 mmol) in dry acetone (2.0 mL), with L-proline (0.10 mmol, 20 mol %) as the catalyst for the specified reaction time and temperature.
Total yield of the inseparable diastereomers (7 and 8) isolated after column chromatography.
Enantioselectivity was determined by HPLC analyses, due to the overlap some of the peaks, the error limits maybe is considerably larger than normal in those cases.
The ratio of 7:8 or vice versa; determined by 1H NMR analyses.
