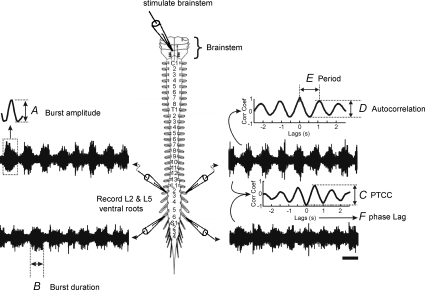
Figure 1. Explanation of parameters measured.
A, burst amplitude, which is determined by high pass filtering the trace and smoothing, rectifying and averaging the burst heights. B, burst duration was calculated by marking the beginning and end of each burst to calculate the average duration. C, the peak to trough correlation coefficient (PTCC) is calculated to compare the stability of the rhythm across different ventral root neurograms, in this case the ipsilateral L2 and L5. D, the autocorrelation coefficient was calculated to quantify the stability of the rhythm in a single root. E, period was obtained from the autocorrelation by calculating the distance between peaks. F, phase lag was determined from the cross-correlogram, with values of 0–1. Alternating rhythms (L2–L2; ipsi L2–L5) are a signature of locomotor-like activity and tend to have a phase lag close to 0.5. Scale bar = 1 s.