Figure 2.
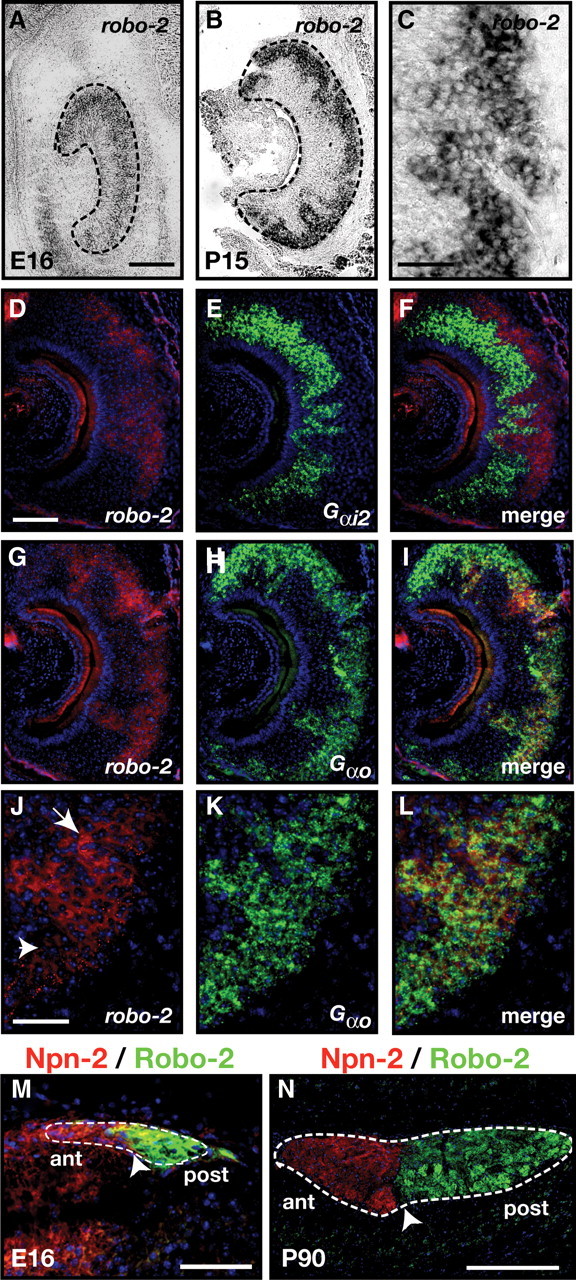
Expression of Robo-2 in vomeronasal sensory neurons. A–L, In situ hybridization of coronal sections of vomeronasal organ isolated from an E16 embryo (A) and P15 mice (B–L) with DIG-labeled cRNA probes specific for robo-2 (A–D, F, G, I, J, L) and fluorescein-labeled cRNA probes specific for Gαi2 (E, F) and Gαo (H, I, K, L). At E16, robo-2 is expressed in vomeronasal neurons while robo-2 expression becomes restricted to vomeronasal neurons located in the basal region of the VNO postnatally (B, C). Robo-2 is not expressed in the Gαi2–expressing vomeronasal neuron population (D–F) while all Gαo vomeronasal neurons express robo-2 (G–L). High-magnification image of vomeronasal neurons coexpressing Gαo and robo-2 reveal that Gαo-positive neurons express high (arrow) or low (arrowhead) levels of robo-2 (J–L). Dotted lines outline the VNO (A, B). Scale bars: 250 μm (A, B, D–I); 125 μm (C, J–L). M, N, Sagittal sections of the accessory olfactory bulb from an E16 embryo (M) and an adult (N) mouse stained with Robo-2 and Neuropilin-2 antibodies. Robo-2 expression is observed exclusively in axons innervating the posterior region of the AOB while Neuropilin-2 expression is restricted to axons innervating the anterior AOB (Cloutier et al., 2002). Dotted lines outline the AOB while arrowheads denote the border between Neuropilin-2 and Robo-2 staining. Scale bars: 50 μm (M); 250 μm (N).
