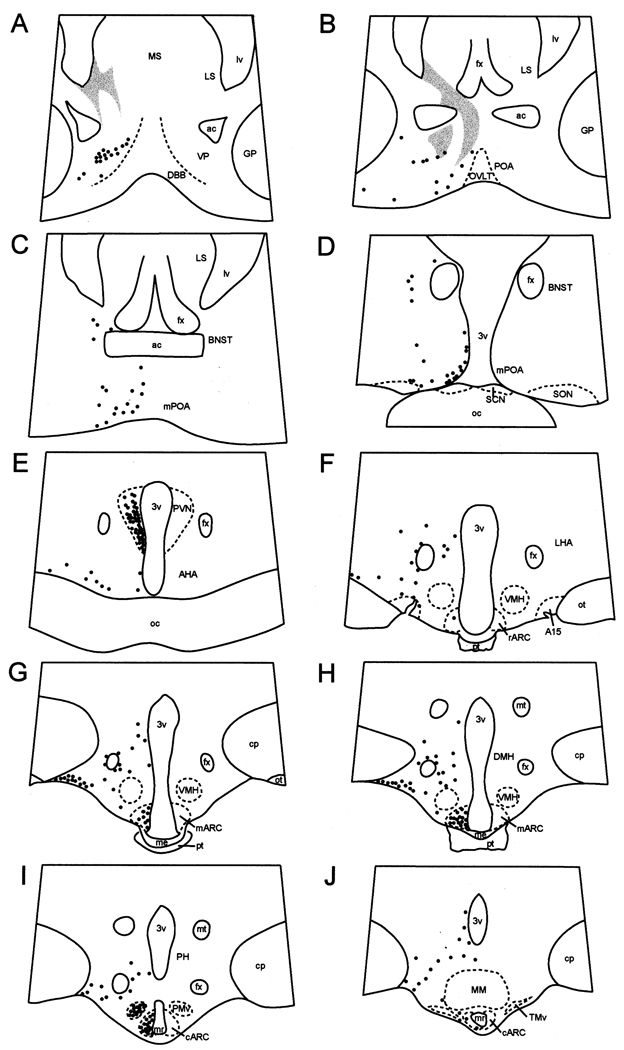
Fig. 1.
Camera lucida drawings of coronal sections depicting the distribution of NK3R-immunoreactive (solid circles) cells in the POA area and hypothalamus of ewes. Shaded areas on panels A and B represent areas of dense fibre labelling in the septum that extends towards the dorsal aspect of the preoptic area. A15, dopaminergic A15 area; ac, anterior commissure; AHA, anterior hypothalamic area; mARC, middle arcuate nucleus; rARC, rostral arcuate nucleus; BNST; bed nucleus of stria terminalis; cp, cerebral peduncle; DBB, diagonal band of Broca; DMH, dorso-medial hypothalamus; fx, fornix; GP, globus pallidus; LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; LS, lateral septum; lv; lateral ventricle; me, median eminence; MM, mammillary body; mr, mammillary recess of the third ventricle; MS, medial septum; mt, mammillothalamic tract; oc, optic chiasma; ot; optic tract; OVLT, organum vasculosum of lamina terminalis; PH, posterior hypothalamus; PMv; ventral premammillary nucleus; POA, preoptic area; mPOA, medial preoptic area; pt, pars tuberalis of the adenohypophysis; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; SCN, suprachiasmatic nucleus; SON, supraoptic nucleus; TMv, ventral tuberomammillary nucleus; VMH, ventromedial hypothalamus; VP, ventral pallidum; 3v, third ventricle.