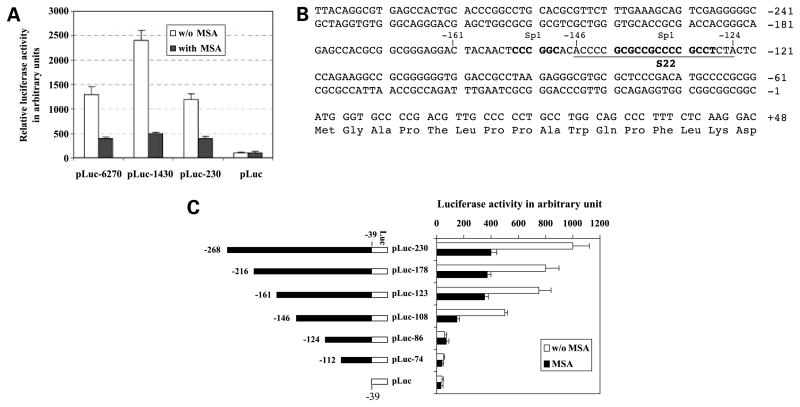
Figure 3.
Identification of cis-element responsible for inhibition of survivin transcription by selenium. A, the inhibitory effect of MSA on survivin transcription was mapped to the survivin core promoter region (230 bp). C4-2 cells were transfected with various survivin promoter –luciferase constructs and treated with or without MSA (5 μmol/L) for 24 h after transfection, followed by luciferase activity assays. B, DNA sequences of the survivin core promoter region (230 bp). Bold letters, Sp1 sites; underlined letters, S22 probe. C, a 37-bp cis-acting DNA element from −161 to −124 bp was identified playing a major role in MSA-mediated inhibition of survivin promoter activity. Left, the indicated survivin constructs were shown in forward orientation upstream of a luciferase reporter gene in pLuc. All the survivin promoter –luciferase constructs are from −39 bp (the ATG translation start site of survivin as +1). Right, C4-2 cells were transfected with different regions of survivin promoter– luciferase constructs and treated with or without MSA (5 μmol/L) for 24 h after transfection, followed by luciferase activity assays. Luciferase activity was normalized to Renilla luciferase and expressed in arbitrary units. Columns, mean from a representative experiment in triplicate; bars, SD.