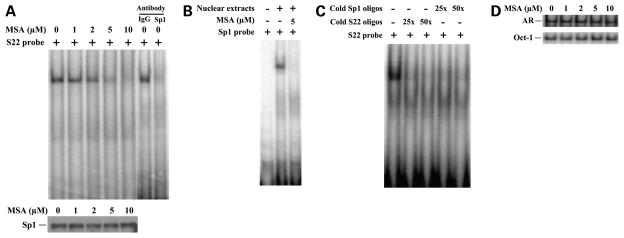
Figure 4.
MSA reduces Sp1 or Sp1-like protein binding to the specific sites in the survivin promoter by EMSA experiments. A, MSA reduces nuclear proteins binding to the 22-bp DNA element (S22) between −146 bp and −124 bp in the survivin promoter by EMSA experiments. C4-2 cells were treated with various doses of MSA as indicated. Nuclear proteins were isolated and used for EMSA experiments with radiolabeled S22 probe (top). Specificity of Sp1 DNA binding was confirmed by supershift with antibody against Sp1 or control antibody against IgG. The expression of Sp1 protein by Western blot analysis using Sp1-specific antibody (bottom). B, the nuclear protein extracts from C4-2 cells treated with or without MSA (5 μmol/L) were used for EMSA experiments with radiolabeled Sp1 probe. C, both cold S22 and cold Sp1 oligos specifically competed with radiolabeled S22-protein complex by EMSA experiments. D, the nuclear protein extracts from C4-2 cells treated with various doses of MSA as indicated were used for EMSA experiments with radiolabeled oligos containing Sp1 binding site in the AR promoter and Oct-1 oligos as the controls.