Fig. 6.
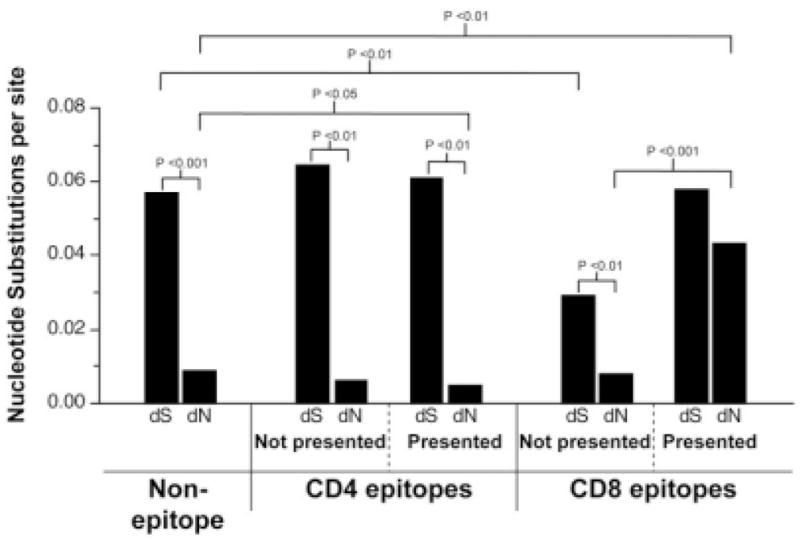
HCV-specific CD8 T cells, but not CD4 T cells, exert significant pressure to drive increased nonsynonymous mutation rates. Median rates of synonymous substitutions per synonymous site (dS) and of nonsynonymous substitutions per nonsynonymous site (dN) were computed separately for nonepitope regions, and for CD4 and CD8 T cell epitopes both in animals that express the specific restricting MHC alleles and in animals that lack the necessary MHC allele to present the epitope to specific CD4 or CD8 T cells (data not shown). Tests of the hypotheses that (1) the median dS is equal to the median dN and (2) an individual dS or dN value in presented epitopes equals that in nonpresented epitopes were performed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Tests of the hypothesis that an individual dS or dN value in epitopes equals that in nonepitope regions were performed using the Mann-Whitney test.
