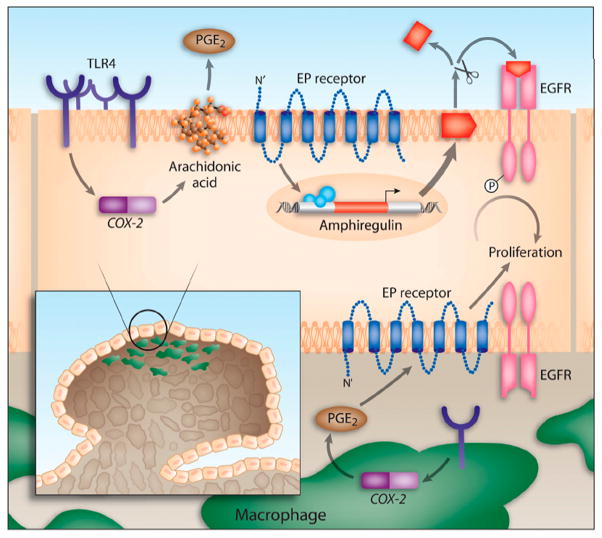
Figure 3. Model of TLR4-mediated colon carcinogenesis (Fukata et al., 2007).
TLR4 expression is increased in chronic intestinal inflammation. TLR4 signaling in response to LPS induces Cox-2 expression and PGE2 production. PGE2 through its receptors can act in a paracrine or autocrine fashion on colonocytes to stimulate the expression and release of amphiregulin, an EGFR ligand. EGFR signaling is associated with increased proliferation of colonocytes. Likewise, TLR4 expression in tumor-associated macrophages may also respond to LPS by inducing Cox-2 and PGE2, which may then act on the epithelium to stimulate proliferation of colonocytes.