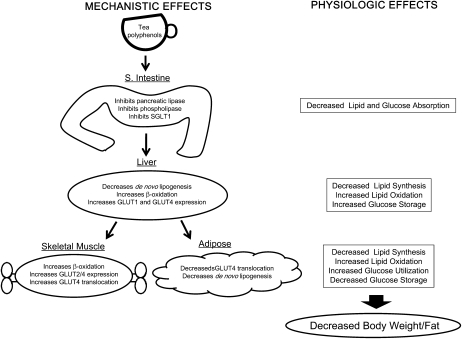
FIGURE 2 .
Reported mechanism(s) by which tea polyphenols may modulate body weight and energy balance. Tea polyphenols have been shown to inhibit de novo lipogenesis, increase lipid oxidation, increase carbohydrate utilization, and decrease carbohydrate uptake. Target tissues include the small intestine, the liver, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle. Abbreviations: S. intestine, small intestine.