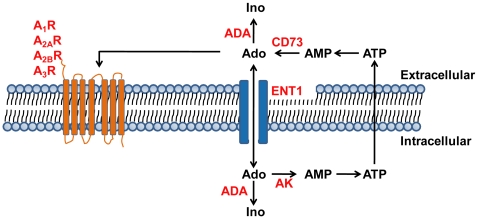
Figure 1. Key components of adenosine metabolism and signaling.
In response to cellular stress and damage, ATP is released into the extracellular space and is rapidly dephosphorylated by extracelluar nucleotidases. CD73 catalyzes the formation of extracellular adenosine from AMP. Extracellular adenosine can interact with seven-transmembrane adenosine receptors, A1R, A2AR, A2BR, and A3R, which are coupled by heterotrimeric G proteins to various second messenger systems, or it can be transported into cells via facilitated nucleoside transporters, such as ENT1. Both extracellular and intracellular adenosine can be deaminated to inosine by adenosine deaminase (ADA). Intracellular adenosine can be secreted or phosphorylated back to ATP. The first step in this process is catalyzed by adenosine kinase (AK).