Figure 1.
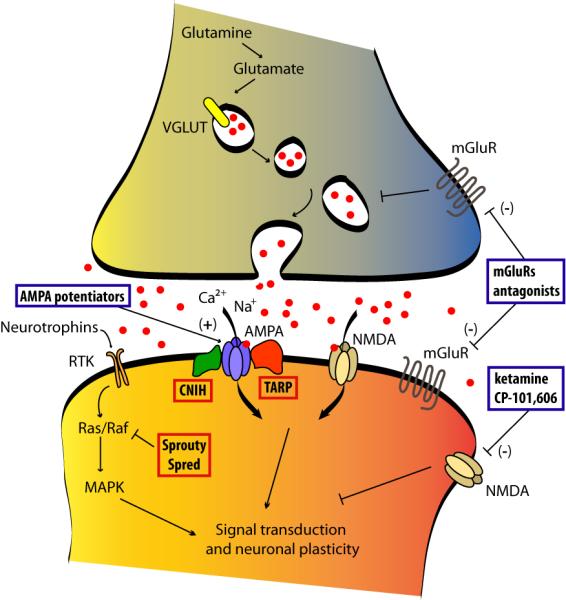
Emerging antidepressant targets from neurotrophic and glutamatergic signaling pathways. Negative modulators of downstream neurotrophic signaling acting at SPROUTY and SPRED protein families represent potential mechanisms for increasing neurotrophic function. AMPA receptor potentiators and NMDA receptor allosteric modulators (with specific subunit selectivity) are now in clinical trials. Allosteric modulators of mGluRs are also being explored in preclinical studies. Modulators of AMPA receptor expression and function, such as TARPs and CNIH, represent potential therapeutic targets as well. Compounds under development for their antidepressants effect are shown in blue boxes. New target proteins are highlighted in red boxes. CNIH, cornichon homolog; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; TARP, transmembrane AMPAR regulatory proteins; VGLUT, vesicular glutamate transporter.
