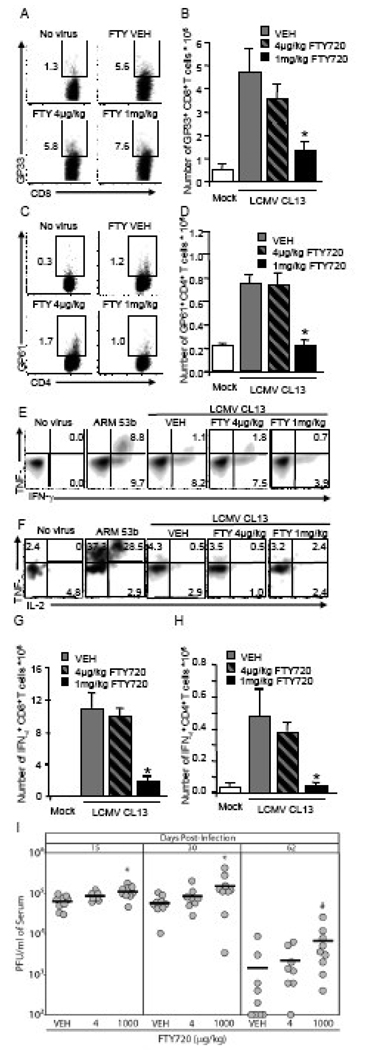
Figure 3. FTY720 does not prevent T cell exhaustion or promote viral clearance, but impairs the T cell immunity in response to LCMV-CL 13 infection.
(A–H) Mice were mock infected (white bars), infected with 1×105 PFU LCMV-Arm53b i.p. (E–F only) or with 2×106 PFU LCMV-Cl 13 i.v. and treated i.v., once a day for 3 days, starting 1 h post-infection with water (VEH; grey bars), 4 µg/kg (dashed bars) or 1 mg/kg (black bars) FTY720, and spleens were harvested on day 8 post-infection. (A–D) Frequencies of CD8+ GP33–41 (A) and CD4+ GP65–77 (C) tetramer positive cells are not altered by FTY720 when compared to VEH. (B and D) Administration of 1mg/kg FTY720 significantly reduces the numbers of these two cell subsets, when compared to vehicle and treatment with 4 µg/kg. (E) GP33–41 peptide stimulation of CD8+ T cells from LCMV-Cl 13-infected mice results in reduced expression of TNF-α and IFN-γ compared to cells from LCMV-Arm53b infected mice. (F) Similarly, IL-2 and TNF-α are strongly produced in response to GP61–80 peptide stimulation from IFN-γ+ CD4+ T cells of mice infected with LCMV-ARM53b, but not with LCMV-CL 13. Treatment with FTY720, at any dose, fails to modify the frequencies of cytokine-producing CD8+ (E) or CD4+ (F) T cells. However, treating with FTY720 at 1mg/kg, but not 4µg/kg, decreases the number of IFN-γ-producing CD8+ (G) or CD4+ (H) T cells, in response to GP33–41 or GP61–80 peptide simulation, respectively, when compared to VEH. (I) Mice were infected with 2×106 PFU LCMV-Cl 13 i.v. and treated i.v., once a day for 3 days, starting 1 h post-infection. Administration of FTY720 at 1mg/kg, but not 4µg/kg, significantly increases LCMV-Cl 13 burden in serum when compared to VEH (n=8–9 mice per group) on days 15 and 30 post-infection. Also 1 mg/kg of FTY720 enhances viral burden and delays LCMV Cl 13 clearance from the serum on day 62 post infection when compared to vehicle-treated mice, but the difference is not statistically significant. (A, C, E, and F) Representative density plots are shown; n ≥ 4 mice per group; average ± SEM; *Significantly different from VEH, p < 0.05. #, p < 0.09.