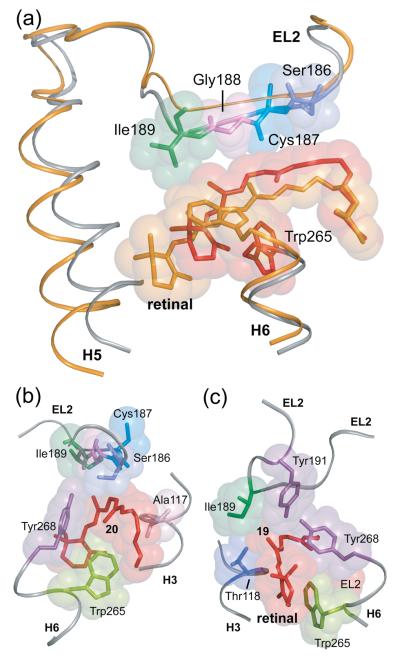
Fig. 4.
Displacement of EL2 upon rhodopsin activation. (A) The β4 strand of EL2 forms a lid of the retinal binding site and is connected to transmembrane helix H5. The rhodopsin crystal structure (gray) is superimposed on the Meta II model (orange) obtained from the guided MD simulations to illustrate the displacement of EL2 needed to satisfy the NMR restraints. (B) and (C) present space filling models of the retinal binding site highlighting the packing of the C20 and C19 methyl groups, respectively. (B) The retinal C20 methyl group is in contact with Trp265 and Tyr268 on H6. Clockwise rotation of the C20 methyl group upon isomerization changes its orientation toward EL2. (C) The C19 methyl group packs against Thr118 on H3, Tyr268 on H6 and Ile189 and Tyr191 on EL2. Counterclockwise rotation of the C19 methyl group would result in a steric clash with Tyr191 and Tyr268, and may be responsible for a shift in the hydrogen bonding interactions involving EL2.