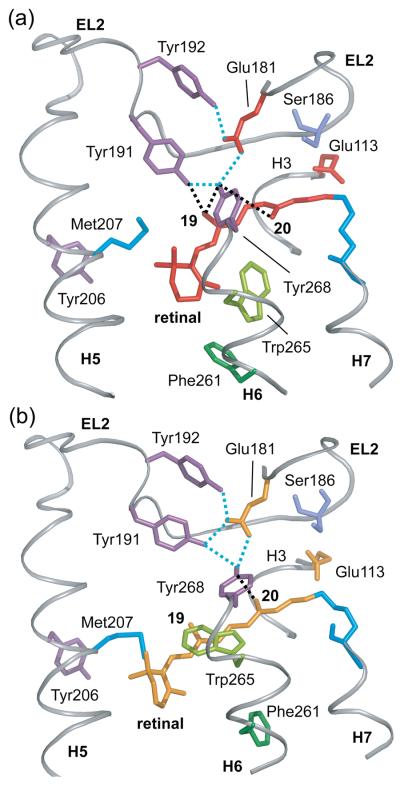
Fig. 6.
Hydrogen bonding changes involving EL2. (A) Crystal structure of rhodopsin highlighting the hydrogen bonding network centered on Glu181. Glu181 is hydrogen bonded (dotted blue lines) to Tyr192 and Tyr191 on EL2 and Tyr268 on H6. Tyr191 is also hydrogen bonded to Tyr268 on H6. Black dotted lines highlight the close interactions between Tyr268 and the retinal C19/C20 methyl groups, and between Tyr191 and the retinal C19 methyl group. (B) The guided MD simulations indicate that retinal isomerization and displacement of EL2 upon activation leads to a rearrangement of the hydrogen bonding network involving Glu181 on EL2. The Glu181 side chain remains hydrogen bonded to Tyr191, Tyr192 and Tyr268 in Meta II. However, Tyr191 is now hydrogen bonded to both Tyr192 and Tyr268. The Meta II model also shows that the retinal C19 methyl group is no longer packed against Tyr191 or Tyr268, although Tyr268 is still in close contact with the retinal C20 methyl group.