Fig. 7.
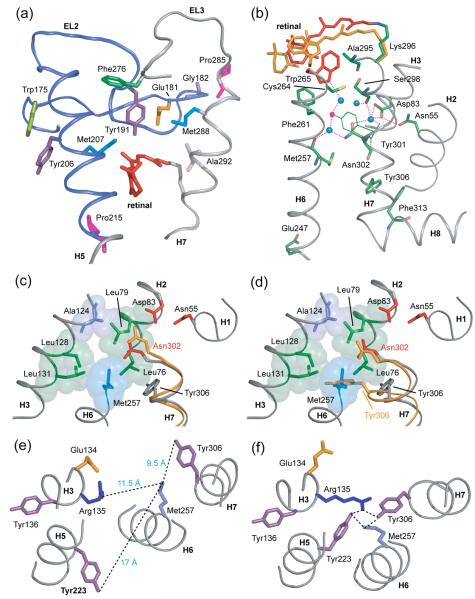
Coupling of retinal isomerization and displacement of EL2 to motion of H7. (A) The extracellular end of H7 contacts EL2 from Pro285 to Ala292. The H5-EL2 segment is presented in blue and EL3-H7 is presented in grey. In rhodopsin, Met288 on H7 is packed against Glu181 on EL2 and Pro285 on EL3 is packed against Gly182 on EL2. The displacement of EL2 upon retinal isomerization and deprotonation of the retinal SB linkage may allow EL3 and H7 to shift into their active conformations. (B) A view of the water-mediated hydrogen bonding network involving H7. The network extends from Trp265 (red; on H6) to Phe313 (green; on H8) through the conserved NPxxY (Asn302…Tyr306) on H7. Blue filled circles represent structural water. Positions of the all-trans retinal and Trp265 from guided MD simulations are shown in orange. In rhodopsin, Trp265 is packed between the side chain of Ala295 on H7 and the retinal β-ionone ring. The Meta II model shows a movement of the Trp265 side chain toward the extracellular side of the receptor away from the water cluster surrounding Asn302 (H7). (C) and (D) present a view of the protein pocket surrounding Asn302 on H7 in rhodopsin. One side of the pocket containing Asn302 is hydrophobic and composed of Leu76, Leu79, Ala124, Leu131 and Leu128. The other side of the pocket is hydrophilic containing Asn55 and Asp83. (C) In the Meta II model from guided MD simulations, Asn302 (orange) shifts toward and hydrogen bonds with Asp83. (D) An overlap of the rhodopsin (grey) and opsin (orange) structures shows a large movement of the side chain of Tyr306 on H7 from its position in rhodopsin to its new position facing H6 in opsin, which was previously occupied by the Met257 side chain on H6. The side chain of Tyr306 is now packed against the surrounding leucine residues on H3 and H2. Asn302 in opsin does not move significantly relative to its position in rhodopsin. (E) and (F) presents the interaction of amino acids around the conserved ERY motif on H3 in rhodopsin and opsin respectively.