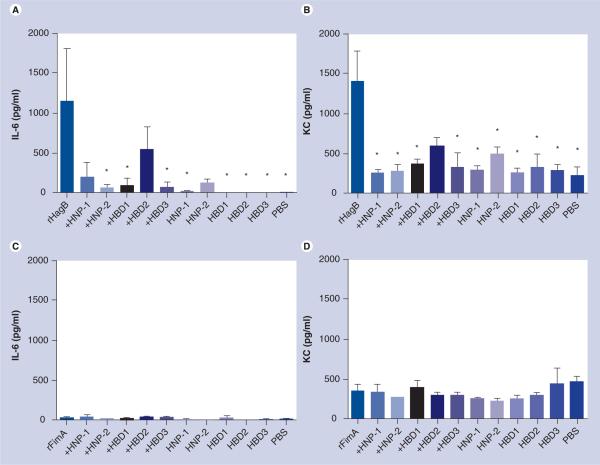
Figure 1. A proinflammatory IL-6 cytokine and keratinocyte-derived chemokine response in the nasal wash fluid of mice exposed intranasally with 10 μg rHagB (A & B) or 10 μg rFimA (C & D) without and with 1 μg HNP1 or 2, and HBD1, 2 or 3.
Mice given rHagB + HNP2, rHagB + HBD1, and rHagB + HBD3 produced significantly lower (p < 0.05) IL-6 responses than mice given rHagB alone (A) and mice given rHagB + HNP1, rHagB + HNP2, rHagB + HBD1, and rHagB + HBD3 produced significantly lower (p < 0.05) KC responses than mice given rHagB alone (B). Mice given rFimA produced very low levels of IL-6 and only moderate levels of KC in nasal wash fluid that were not attenuated by prior incubation of rFimA with any defensin (C & D). Bars represent the mean with standard errors of the mean.
*p < 0.05, treated versus rHagB control (significance was based on the log10 transformed data).
HBD: Human β-defensin; HNP: Human neutrophil peptide α-defensin; KC: Keratinocyte-derived chemokine; PBS: Phosphate-buffered saline; rFim: Recombinant fimbrillin; rHag: Recombinant hemagglutinin.