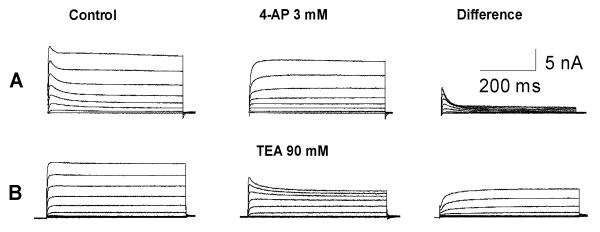
Figure 1.
Pharmacological isolation of the K current reveals 2 distinct classes of small DRG neurons. A: A typical neuron with a large amount of non-inactivating sustained component and a smaller component of rapidly inactivating transient component. B: A typical small neuron with both non-inactivating sustained and fast inactivating components. Note that the rapidly inactivating component is sensitive to 4-AP; and the non-inactivating sustained component is blocked by TEA.