Fig. (2). The G Protein Cycle.
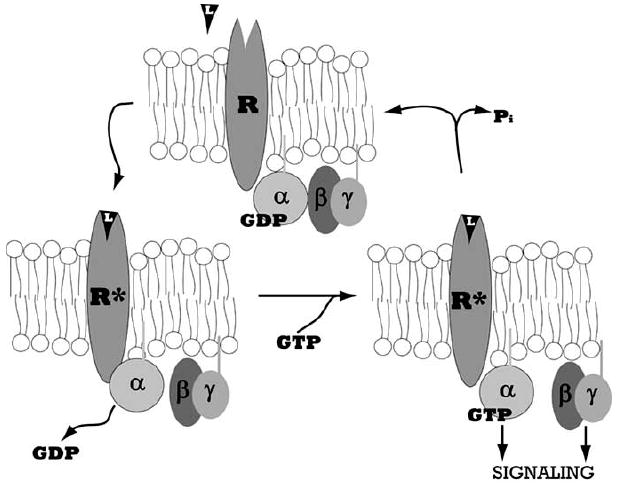
Heterotrimeric G proteins comprise three subunits, α, β, and γ, which associate in the inactive Gα-GDP bound state. The seven transmembrane domain G protein coupled receptor (GPCR), denoted by R, is activated by ligand binding, L. The activated receptor, denoted by R*, associates with Gα and catalyzes the dissociation of GDP. The subsequent binding of GTP causes Gα to dissociate from Gβγ, exposing interaction sites on Gα and Gβγ through which these proteins can activate downstream effectors and transduce signals. Subsequent hydrolysis of GTP to GDP by the intrinsic GTPase activity of Gα causes inactivation and reassociation of the Gαβγ complex.
