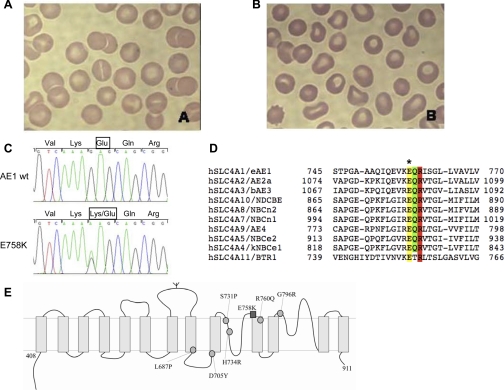
Fig. 1.
The novel AE1 spherostomatocytosis mutation E758K. A and B: peripheral blood Wright-Giemsa smears from patients 1 and 2, respectively. C: partial nucleotide sequence of exon 17 of the SLC4A1 gene from a normal control [wild-type (wt); top] and from patient 2 (bottom). Heterozygosity for the G-to-A mutation at nucleotide 2272 is evident in the sequence from patient 2. Exon 17 from patient 1 DNA exhibited the identical mutation (not shown). D: sequence alignment of part of the human erythroid AE1 (eAE1) transmembrane domain with corresponding regions from other SLC4 polypeptides. Note conservation of AE1 E758 (yellow band with ∗ above) adjacent to Q759 (green band, site of a distal renal tubular acidosis mutation) and R760 (red band, site of a hereditary spherocytosis mutation associated with cation leak). Amino acid residue numbers bracket each sequence. E: schematic diagram of the transmembrane domain of AE1, showing putative location of AE1 E758K (dark square) and previously reported AE1 stomatocytosis mutations (light circles).