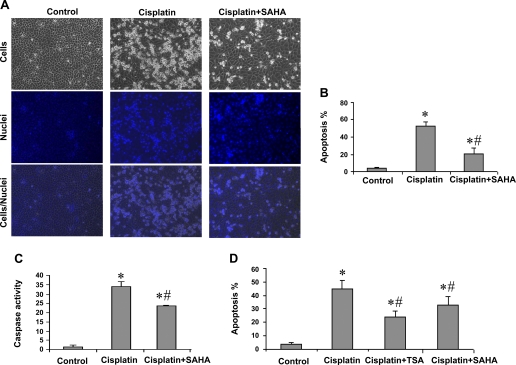
Fig. 1.
Inhibition of cisplatin-induced apoptosis in renal proximal tubule cells (RPTC) by suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) and trichostatin A (TSA). A, B, and C: RPTCs were pretreated for 6 h without or with 5 μM SAHA and then incubated for 18 h with 20 μM cisplatin or 20 μM cisplatin plus 1 μM SAHA. D: cells were pretreated for overnight without or with 1 μM SAHA or 0.1 μM TSA and then incubated with 20 μM cisplatin or 20 μM cisplatin plus 1 μM SAHA or 0.1 μM TSA for 24 h. Control cells were not exposed to SAHA, TSA, or cisplatin. A: morphology. Cells were stained with 10 μg/ml Hoechst33342 to record nuclear and cellular morphology by fluorescence and phase-contrast microscopy. B: percentage of apoptosis. Apoptotic cells were counted by morphology to determine % apoptosis. C: caspase activity. Cell lysate was collected to measure caspase activity in an enzymatic assay. D: percentage of apoptosis. Cells were evaluated by morphology to determine % apoptosis. B, C, and D: data are expressed as means ± SD (n = 3–4). *Statistically significantly different from the control. #Statistically significantly different from the cisplatin-alone group.