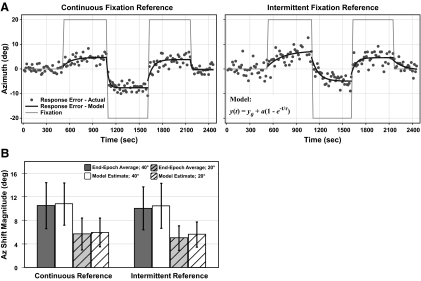
Fig. 3.
Sound localization during horizontal gaze shifts with continuous or intermittent visual fixation reference. A: sound localization accuracy (error between response and target location) in Az is shown during either continuous (left) or intermittent (right) presentation of a fixation reference for a representative subject. Each session consists of 5 continuous epochs in which fixation was cued by laser-projected spots that alternated between center, right 20°, and left 20° (thin gray trace). Responses are offset by average pointer error during the initial epoch of central fixation. Errors for individual trials (filled circles) show a shift in localization over time in the direction of fixation. The exponential model (black trace; see equation at right) predicted time constants (τ, s) and shift magnitudes (a, °) for each epoch. Average shift magnitude across all 4 sessions (2 shown here) is comparable between conditions, whereas the time constant is more prolonged for the intermittent than the continuous condition (P < 0.01). B: average shift magnitude in response to 40 and 20° gaze shifts (each pooled for L and R) during continuous and intermittent fixation references, calculated as end-epoch averages (Δ accuracies between epochs) and model estimates (a). Values are comparable between calculation methods and reference conditions (P ≥ 0.55). Error bars indicate SD across 9 subjects. The format and conventions here apply to similar figures except as noted.