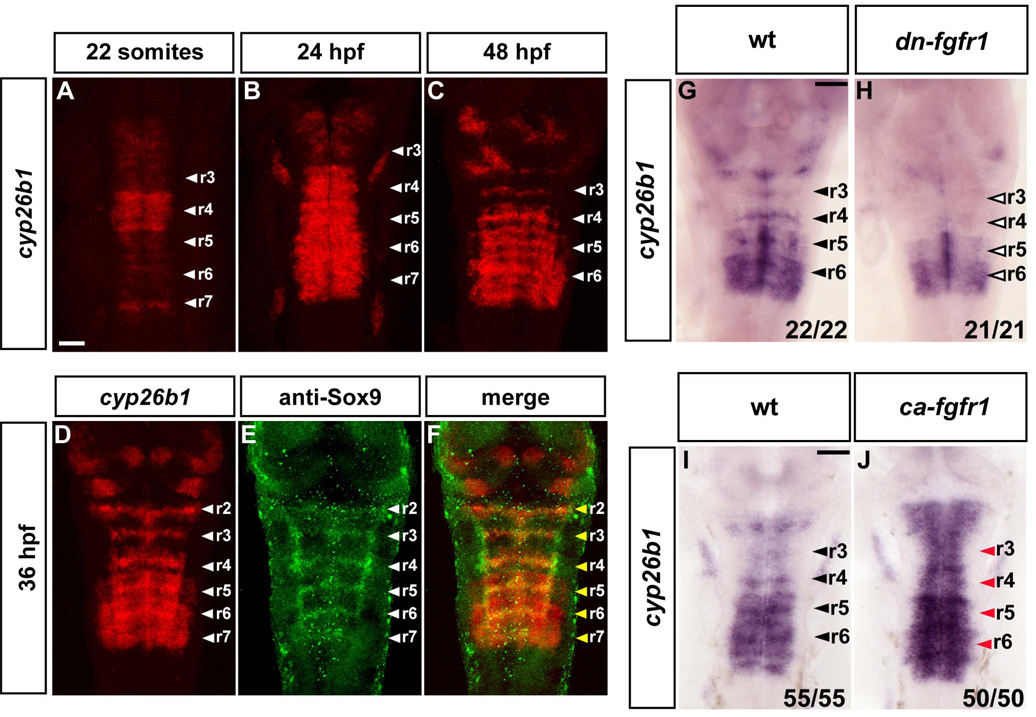
Figure 4. Cyp26b1 is expressed in segment centres and regulated by FGF signaling.
(A–D): In situ hybridisations to detect the time course of cyp26b1 expression. Images are a merge of confocal stacks of Fast Red staining. Scale bar, 50 µm. White arrowheads indicate segment centres. (D–F): In situ hybridisation of cyp26b1 followed by immunostaining with anti-Sox9 antibody. Yellow arrowheads show colocalization of cyp26b1 with Sox9b in segment centres. (G–H): In situ hybridization of 40 hpf embryos to detect cyp26b1 expression in wild type (wt; G) or dominant negative FGFR1 embryos (Tg(hsp70l:dnfgfr1-EGFP)) (H). Heat shocks were started at the 22 somite stage. Black arrowheads indicate segment centres, and open arrowheads indicate the disappearance of cyp26b1 expression from centres. Scale bar, 50 µm. (I–J): In situ hybridization of 26 hpf embryos to detect cyp26b1 in either wild type (wt; I) or constitutively active fgfr1 embryos, Tg(hsp70:ca-fgfr1) (J). Heat shocks were started at 24 hpf and embryos fixed 2 h later. Black arrowheads indicate segment centres, and red arrowheads centres in embryos with cyp26b1 upregulation. Scale bar, 50 µm.