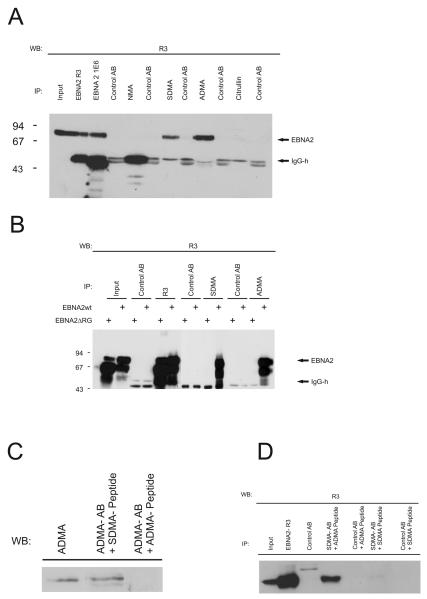
Fig. 2.
Detection of methylated EBNA2 species. (A) Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) directed against the non-methylated (NMA), sDMA-, aDMA-, or citrulline containing Arginine-Glycine (RG)-repeat of EBNA2 were tested by precipitation using extracts of EBV-positive B95.8 cells. For each antibody, an appropriate isotype control was tested in parallel to exclude unspecific binding to the protein G sepharose. Precipitated EBNA2 protein was visualized using the EBNA2-specific mAb R3 which binds outside the RG-domain of EBNA2. (B) Immunoprecipitation of EBNA2 from transiently transfected cells. HEK 293-T cells expressing either EBNA2-wt or the EBNA2-RG mutant were precipitated with R3 and the various methylation specific monoclonal antibodies as indicated using appropriate isotype control antibodies. The position of EBNA2 is indicated by an arrow. (C) Specific inhibition of aDMA-antibody by aDMA peptide. The aDMA-specific antibody 6F12 was used in a Western blot either untreated or pre-incubated with aDMA or sDMA-peptide as indicated. (D) Specific inhibition of sDMA-antibody by sDMA peptide. Extract of B95.8 cells was used for immunoprecipitation using either untreated or antibody 7D9 preincubated with aDMA or sDMA peptide. Irrelevant control antibody was used as an internal control. Precipitated EBNA2 was detected by Western blot using the R3 antibody.