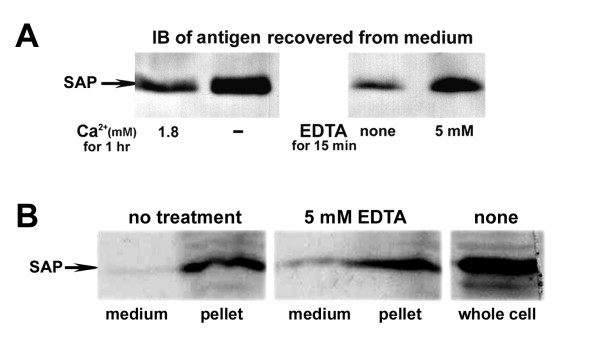
Figure 4.
The majority of SAP molecules bind to the human sperm surface in a calcium-independent fashion. SAP is slowly released from the surface of washed, swim-up harvested human sperm when incubated in a Ca2+-free DMEM medium (A, left panel). The addition of 5 mM EDTA to the medium induced a similar strong discharge of surface bound SAP within minutes (A, right panel). However, most SAP antigens remained attached to the sperm, despite the removal of calcium from the medium (B).