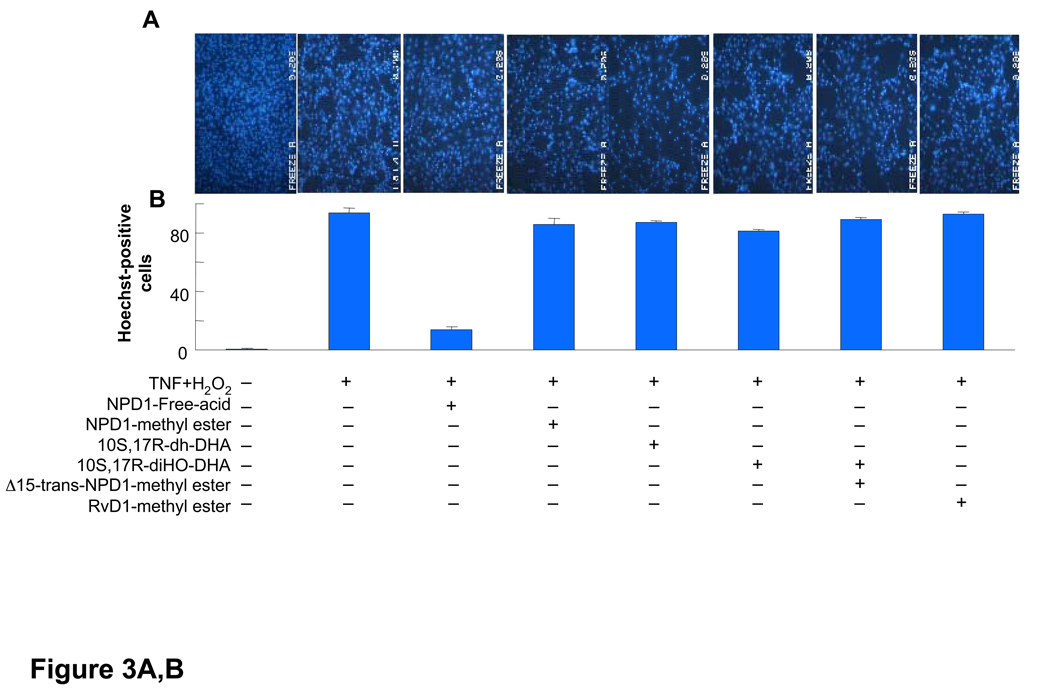
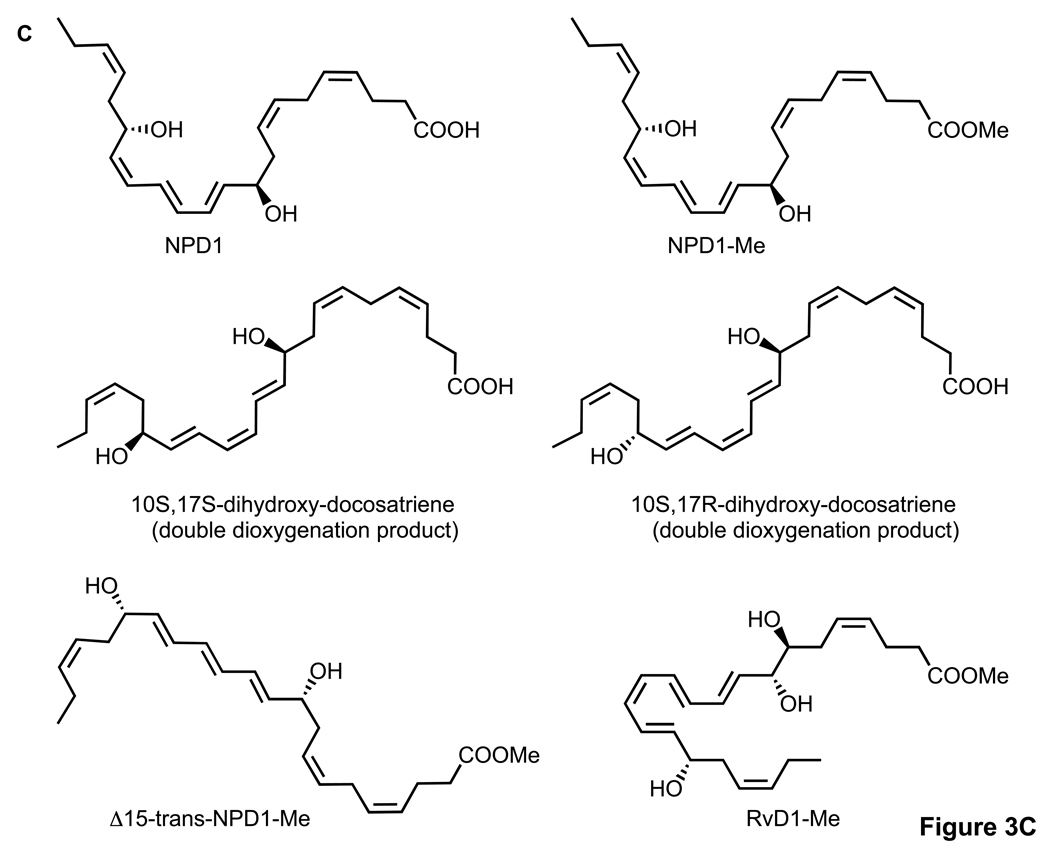
Figure 3.
Activity of NPD1, its stereoisomers and related compounds on oxidative stress (OS)-induced apoptosis in ARPE-19 cells. Evaluation of neuroprotective bioactivity in ARPE-19 cells under OS induced by 600 µM H2O2 and 10 ng/ml TNF-α. Cells grown for 72 h after plating were serum starved for 8 h before OS induction. Compounds were added (50 nM) at the time of OS induction. After 14 h of treatment, cells were 33342 Hoechst stained, and apoptotic cells scored as described in Materials and Methods. Hoechst 33342 nuclear staining in these conditions correlates with oligo- and mono nucleosomes formation, [3H]-thymidine DNA degradation, and caspase-3 activation, additional assays of monitoring cell death [2]. (A) Representative pictures of ARPE-19 cells stained with 33342 Hoechst. Apoptosis (condensed and shiny nuclei) upon exposure to OS, and OS + NPD1 or other lipids. (B) Quantitative analysis of apoptotic cell populations. Results are expressed as percent of total population and are average of three independent experiments, ± standard error (SE). (C) Chemical structures of NPD1, NPD1 methyl ester (NPD1-Me), 10S,17S-dihydroxy-docosatriene, 10S,17R-dihydroxy-docosatriene, 10S,17S-dihydroxy-docosatriene, Δ15-trans-NPD1-Me and resolvin D1-Me.