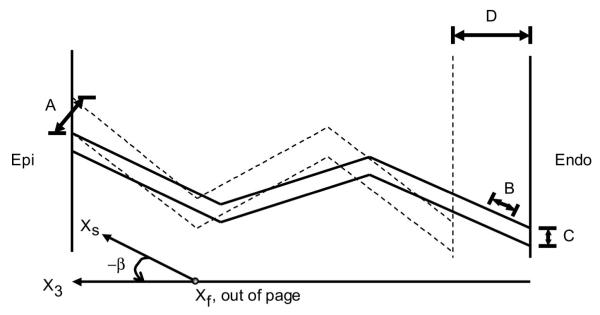
Fig. 6.
Two-dimensional representation of the plane, which in reality twists through the wall, as the sheets are perpendicular to the helically progressing fibers across the wall. Solid and dashed lines, lateral myolaminar sheets in systole and diastole, respectively. With alternating sheet families through the wall, wall thickening (D) may be due to laminar transverse shear (A), laminar extension (B), and laminar thinning (C) of each population.