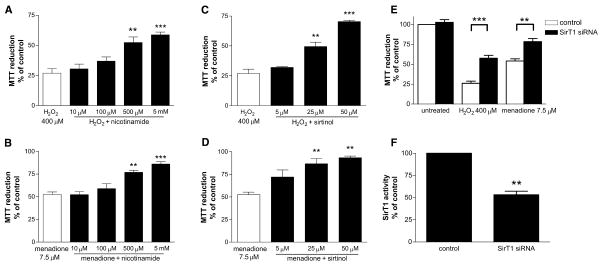
Figure 1.
Inhibiting SirT1 deacetylase increases oxidative stress resistance in neurons. Cortical neurons were cultured in 96-well plates (A–E) or 10 cm dishes (F). (A, B, C, D) 10–14 DIV neurons were treated with nicotinamide (A, B; Nico) or sirtinol (C, D) at indicated concentrations for 48 hrs. Oxidative stress was then induced by 400 μM of hydrogen peroxide (A, C) or 7.5 μM of menadione (B, D), respectively. 24 hrs later cell viability was measured by MTT assay. The ODs are normalized to respective controls (H2O2/menadione relative to vehicle-treated control; H2O2+Nico/sirtinol relative to Nico/sirtinol alone; menadione+Nico/sirtinol relative to Nico/sirtinol alone). (E) 5 DIV neurons were transfected with control or SirT1 siRNA. 2 days later some neurons were subjected to H2O2 or menadione, followed by MTT assay 24 hrs later. (F) 5 DIV neurons were transfected with control or SirT1 siRNA and 2 days later SirT1 deacetylase activity was measured. Data represent mean±SEM.