Figure 8.
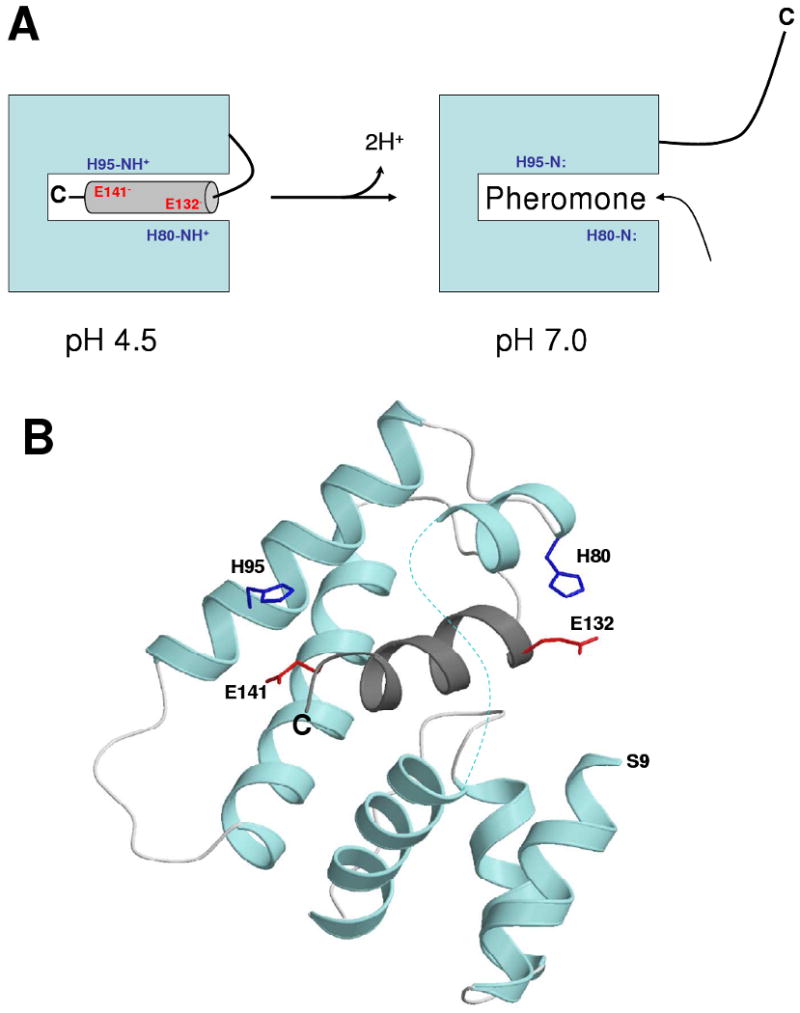
Schematic model showing pH-dependent pheromone binding regulated by a histidine protonation switch (A) and atomic structure highlighting histidine salt bridges (B). Acidic-induced salt bridges (H80/E132 and H95/E141) stabilize insertion of the C-terminal helix (α7) at pH 4.5. At pH 7, H80 and H95 become unprotonated (neutral) and promote extrusion of the C-terminal helix. A hydrophobic sex pheromone structurally resembles the C-terminal helix and binds inside the hydrophobic cavity at pH 7.
