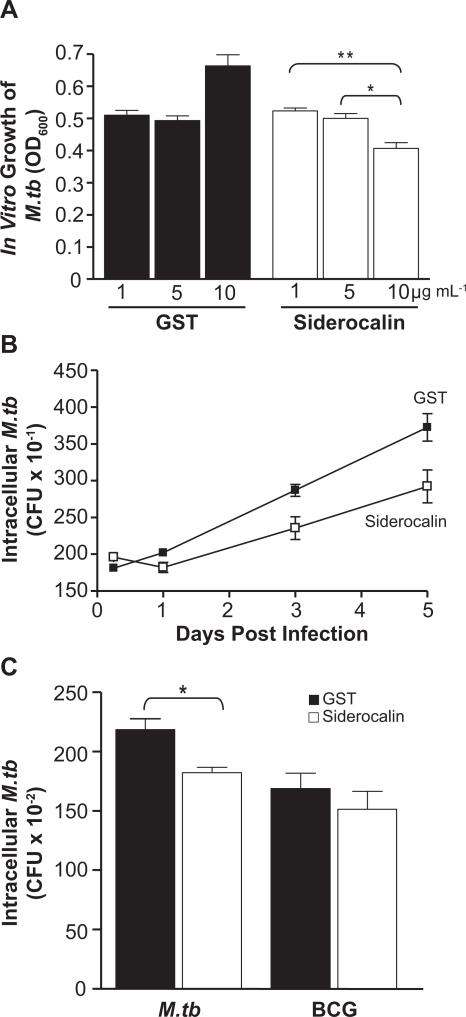
FIGURE 4. Recombinant siderocalin inhibits M.tb growth.
(A) 3 × 104 CFU mL−1 of M.tb was grown in 7H9 broth containing the indicated concentrations of GST or GST-siderocalin. Growth was assayed by determining the OD600. For statistical analysis, the means ± SEM from a single experiment (n=3) are shown. (**) denotes P ≤ 0.01, (*) denotes P ≤ 0.05 using the Student's t test. (B) RAW264.7 cells were infected with M.tb at an MOI of 1:1. 10 μg mL−1 GST or GST-siderocalin was added to the culture medium daily over the time course. The replication of intracellular bacteria was assessed by determining CFU. The means ± SEM from one experiment (n = 3) are shown. Statistical analysis using two-way ANOVA determined that the curves were significantly different P < 0.0001. (C) RAW264.7 cells were infected with M.tb or BCG at an MOI of 1:1. 10 μg mL−1 GST or GST-siderocalin was added to the culture medium daily for 3 days. The replication of intracellular bacteria was determined by counting CFU. The means ± SEM from one experiment (n = 3) are shown. (*) denotes P ≤ 0.05 using the Student's t test. For all experiments, similar results were obtained on separate occasions.