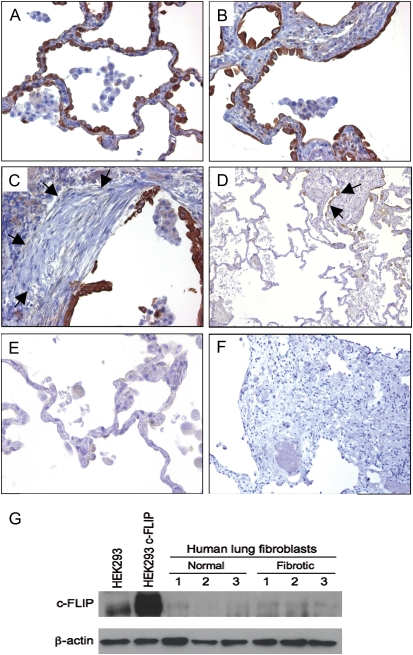
Figure 2.
c-FLIP expression in lung tissues from patients with IPF/UIP. (A–C) c-FLIP was localized to alveolar epithelial cells including areas of mild injury and septal thickening (A and B) and cells overlying fibroblastic foci (C; arrows denote location of fibroblastic focus). c-FLIP was not detected in the mesenchymal cells of the fibroblast foci (C). Weak staining was seen in alveolar macrophages (A–C). (D) Low-power image showing alternating normal and fibrotic lung tissue. Note the absence of c-FLIP staining in areas of normal lung tissue, and positive c-FLIP staining in epithelial cells in a fibrotic area (denoted by arrows). (E) High-power image showing the lack of c-FLIP staining in a normal area of lung tissue in a patient with IPF/UIP. (F) Control stain with nonimmune IgG and secondary antibody (A, B, C, and E: ×20 objective; D and E: ×4 objective). (G) Immunoblot for c-FLIP showing low to undetectable expression of c-FLIP in lysates from primary fibroblasts isolated from lung tissues of nondiseased subjects and patients with IPF/UIP. HEK293 cells and HEK293 cells transfected with a c-FLIP expression construct were used as positive controls. An immunoblot for β-actin shows that equal amounts of total protein were loaded onto each lane.