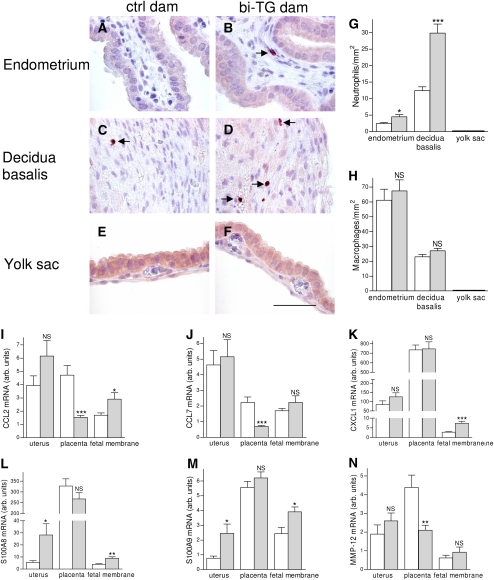
Figure 2.
Maternal inflammation. Pregnant bi-TG and control dams received doxycycline in drinking water from E0 until dams were killed at E14. (A–F) Immunohistochemical staining for neutrophils in the endometrium, decidua basalis, and yolk sac. (G) Neutrophil counts in uterine and gestational tissues. Bi-TG dams had significantly higher numbers of neutrophils in the endometrium and decidua basalis, but no neutrophils were seen in the fetal membranes (yolk sac and amnion). (H) Macrophage counts in uterine and gestational tissues. The number of macrophages in endometrium, decidua basalis, or fetal membranes (yolk sac and amnion) was not affected by maternal genotype. No macrophages were detected in the fetal membranes. (I–N) mRNA expression of inflammatory genes in uteri, placentas, and fetal membranes (yolk sac and amnion). Expression of S100A8 and S100A9 was increased in the uteri of bi-TG dams, whereas the expression of CCL2, CCL7, and MMP-12 was decreased in placentas from bi-TG dams. Open bars, control dams; gray bars, bi-TG dams; NS, not significant; n ≥ 5; *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001 control dams versus bi-TG dams. Scale bar, 50 μm.