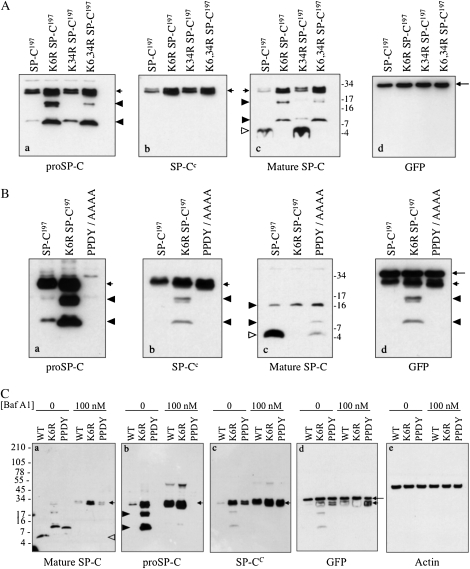
Figure 3.
Effect of K6 and PY motif mutations on trafficking and processing of proSP-C. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with WT proSP-C (SP-C1–197) or proSP-C in which K6 and/or K34 were mutated to arginine. Cell lysates were prepared 24 hours after transfection and analyzed by SDS-PAGE/Western blotting. Blots were serially probed with antibodies directed against proSP-C (a), the C-terminal, lumenal domain of proSP-C (b), mature SP-C (c), or GFP (d). Short arrows indicate proSP-C; open arrowhead indicates mature peptide; closed arrowheads indicate proSP-C processing intermediates; and long arrow indicates GFP (expressed from the pIRES2-EGFP vector). (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with WT proSP-C or proSP-C carrying a K6R mutation or PPDY/AAAA (PY motif) mutation. Cell lysates were prepared 24 hours after transfection, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE/Western blotting. Blots were serially probed with the indicated antibodies, as described for (A). Incomplete stripping between blots resulted in detection of proSP-C (short arrows), processing intermediates (closed arrowheads), in addition to GFP (long arrow) in (d). proSP-C carrying the PPDY/AAAA mutation was not detected by antibody directed against the N-terminal peptide of proSP-C ([a], short arrow), but was detected by antibody directed against the lumenal domain of proSP-C ([b], short arrow). (C) HEK293 cells were transfected as described in (B), and treated with bafilomycin A1 for 4 hours. Cell lysates were prepared 24 hours after transfection, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE/Western blotting. Blots were serially probed with the indicated antibodies. Short arrows indicate proSP-C; closed arrowheads indicate processing intermediates; open arrowhead indicates mature peptide; and long arrow indicates GFP. GFP expression (d) indicates equivalent expression of SP-C constructs; actin expression (e) indicates equivalent loading of samples on gel.