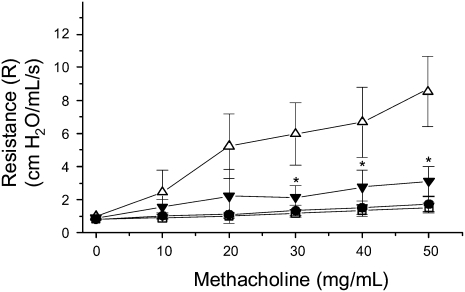
Figure 1.
Moderate-intensity aerobic exercise attenuates airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) in ovalbumin (OVA)-treated mice. Mice were OVA treated and exercised as described in Materials and Methods (open squares: sedentary, saline-treated; open circles: exercised, saline-treated; open triangles: sedentary, OVA-treated; solid triangles: exercised, OVA-treated). At the conclusion of the protocol, mice were assessed for changes in AHR via mechanical ventilation with methacholine challenge at increasing concentrations. Results are presented as total lung resistance (cm H2O/ml/s; *P < 0.02, as compared with sedentary, OVA-treated mice; n = 6–8 mice per group).