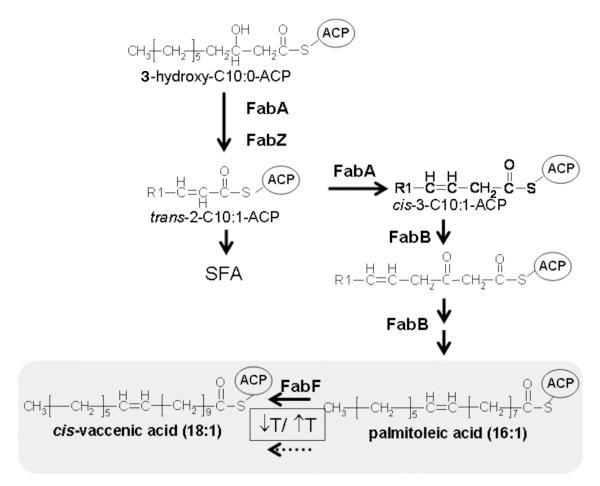
Fig. 1.
The anaerobic pathway of unsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis in E. coli. The 3-hydroxylacyl-ACP intermediate is dehydrated by either FabA or FabZ. FabA catalyzes the first committed step in UFA synthesis, the isomerization of the double bond of the 10-carbon intermediate. 3-Ketoacyl-ACP synthase I (KASI or FabB) is required for condensation of malonyl-ACP with the cis-3-C10:1-ACP. Further elongation of the unsaturated fatty acyl-ACP intermediates can be carried out by either FabB or FabF (KAS II) to produce a 16-carbon monounsaturated fatty acid, palmitoleate. Elongation of 16:1 to 18:1 is catalyzed by KAS II. However, at high temperatures (42 °C), KAS II is inactive and palmitoleate accumulates. The major UFA species are shaded. The R1 group is CH3-(CH2)5.