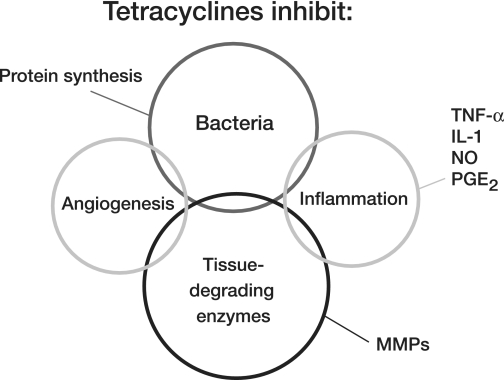
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of action of tetracyclines. Tetracyclines have several non-antimicrobial effects. The ability of these drugs to inhibit matrix metalloproteinases is well established. Based on this mechanism, tetracyclines have shown clinical effects on rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis. Doxycycline and minocycline are the two tetracyclines that have been studied most extensively. TNF: tumor necrosis factor; IL: interleukin; NO: nitric oxide; PG: prostaglandin.