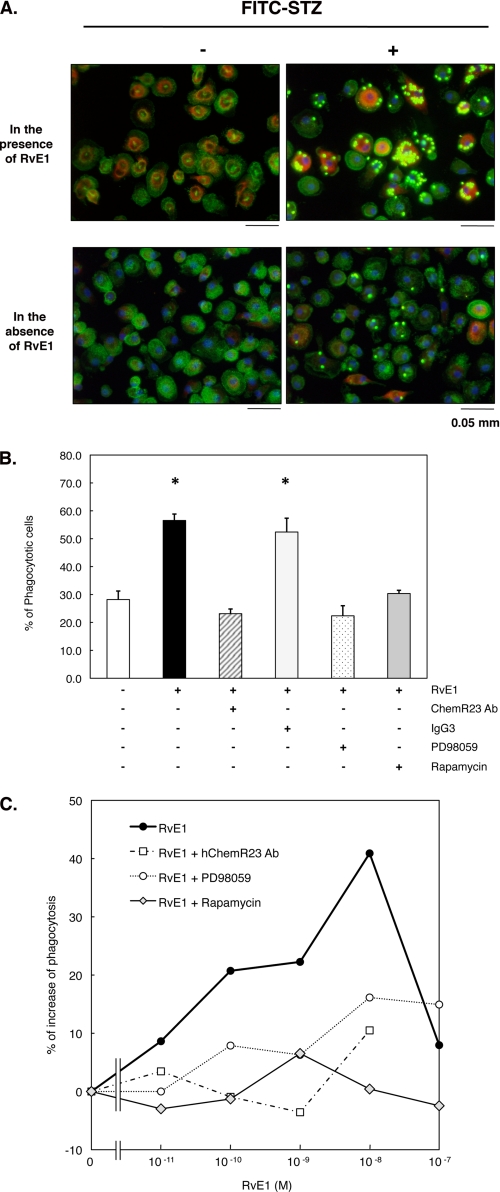
FIGURE 7.
RvE1 enhances phagocytosis of FITC-STZ in human macrophages. A, RvE1-induced FITC-STZ uptake and rS6 phosphorylation in human macrophages. Macrophages (4-well chamber slides, 0.5 × 106 cells/well) were treated with RvE1 (10 nm, 37 °C, 15 min) followed by co-incubation with or without FITC-STZ (green particles, 2.5 × 106 particles/well) for 30 min at 37 °C. Cells were stained with anti-phospho-rS6 (Ser235/Ser236) Ab using Alexa Fluor® 568 secondary Ab (red) to detect the phosphorylated form of rS6. Actin filaments were labeled with Alexa Fluor® 488-phalloidin (green), and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). B, reduction of agonist-enhanced phagocytosis of FITC-STZ by pharmacological inhibitors. Cells were treated with ChemR23 Ab (1:100 dilution), isotype control IgG3 (1:100), PD98059 (50 μm), or rapamycin (20 nm) for 15 min followed by RvE1 stimulus (10 nm, 37 °C, 15 min) and co-incubation with FITC-STZ (30 min, 37 °C). Phagocytosis was assessed by counting the percentage of cells ingesting FITC-STZ particles. Results represent the mean values ± S.E. for three separate experiments (*, p < 0.05 when compared with cells incubated with vehicle alone plus FITC-STZ). C, concentration-dependent increase in phagocytosis of FITC-STZ by human macrophages exposed to RvE1. Cells (96-well plate, 0.1 × 106 cells/well) were pretreated with ChemR23 Ab (1:100 dilution), PD98059 (50 μm), or rapamycin (20 nm) for 15 min. Cells were then treated with the indicated concentration (0.01–100.0 nm) at 37 °C for 15 min followed by co-incubation with FITC-STZ for 30 min at 37 °C. Phagocytosis was quantified using a fluorescent plate reader as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Results are representative of at least three separate experiments and are expressed as the percent of fluorescent intensity above cells incubated with vehicle alone plus FITC-STZ.