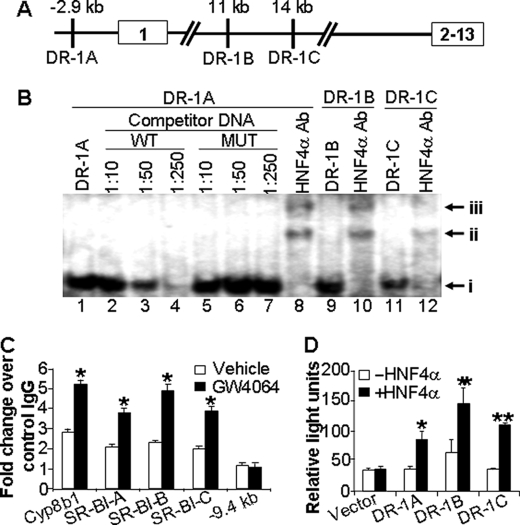
FIGURE 5.
SR-BI is a direct target of HNF4α. A, diagram showing the three putative DR-1-binding sites in the promoter or intron 1 of the mouse SR-BI gene. Exons are boxed. Distances are given from the transcriptional start site. B, EMSAs were performed. Band i represents the complex of HNF4α protein with DR-1A, DR-1B, or DR-1C (lanes 1, 9, and 11). The DNA-protein complexes were supershifted in the presence of HNF4α antibody (lanes 8, 10, and 12; bands ii and iii). MUT, mutant; WT, wild type. C, wild-type mice were treated with vehicle or GW4064 for 7 days. Liver lysates (n = 3 mice per group) were used for chromatin immunoprecipitation assays to determine the binding of HNF4α protein to DR-1A, DR-1B, DR-1C, or a sequence that does not contain any DR-1 element at −9.4 kb of SR-BI gene or a known DR-1 element in the Cyp8b1 gene (positive control). The results are shown in fold changes relative to the basal levels obtained using mouse IgG (control). D, triplicate dishes of HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids expressing HNF4α and β-galactosidase, together with a TK-luciferase reporter construct containing either SR-BI DR-1A-, DR-1B-, or DR-1C-binding sites or the empty vector. After 48 h, cells were harvested, and luciferase activities were determined and normalized to β-galactosidase activities. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus the absence of HNF4α.