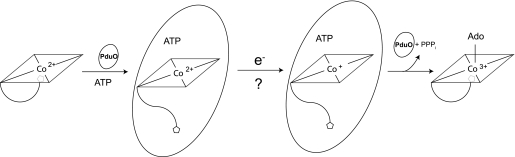
FIGURE 1.
Proposed mechanism for the reduction and adenosylation of cobalamin. PduO-type ACA enzymes (oval) bind 5-coordinate cob(II)alamin and facilitate its reduction to cob(I)alamin by displacing the lower ligand. The latter event generates a 4-coordinate cob(II)alamin intermediate whose redox potential is raised enough so it can accept one electron from dihydroflavin. The resulting cob(I)alamin nucleophile attacks ATP to generate coenzyme B12 (AdoCbl) and triphosphate. In these studies, we investigated the source of the electron for the reduction of cob(II)alamin to cob(I)alamin.