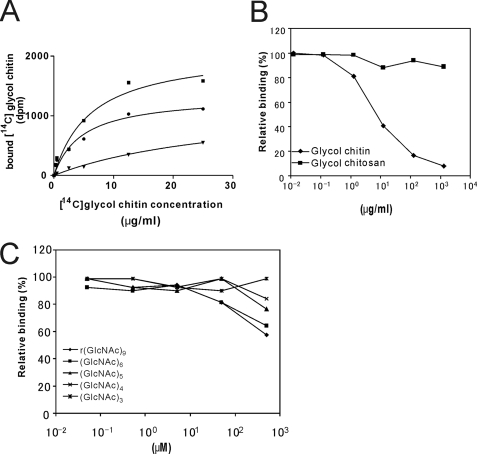
FIGURE 6.
Binding of [14C]glycol chitin to LysM RLK1-yEGFP. A, 40 pmol of LysM RLK1-yEGFP bound to nickel-chelating Sepharose was incubated with 0.025, 0.5, 2.5, 5, 12.5, and 25 μg/ml at room temperature for 30 min in the absence of (■, total binding) or presence of (▾, nonspecific binding) 100-fold unlabeled glycol chitin. To determine the specific binding (●), nonspecific binding was subtracted from total binding. B, competition of the binding of [14C]glycol chitin to LysM RLK1-yEGFP by the unlabeled glycol chitin. 40 pmol of LysM RLK1-yEGFP bound to nickel-chelating Sepharose was incubated with various concentrations of glycol chitin and glycol chitosan (0.125, 1.25, 12.5, 125, and 1250 μg/ml) and then incubated with 12.5 μg/ml [14C]glycol chitin at room temperature for 30 min. C, competition of the binding of [14C]glycol chitin to LysM RLK1-yEGFP by chitin oligosaccharides. 40 pmol of LysM RLK1-yEGFP bound to nickel-chelating Sepharose was incubated with various concentrations of chitin oligosaccharides (0.05, 0.5, 5, 50, and 500 μm) and then incubated with 12.5 μg/ml [14C]glycol chitin at room temperature for 30 min. The relative percentage binding was calculated by comparison with the dpm in the absence of competitors (100% binding). The experiments were repeated three times (A) or twice (B and C), and the averages of the results are shown.