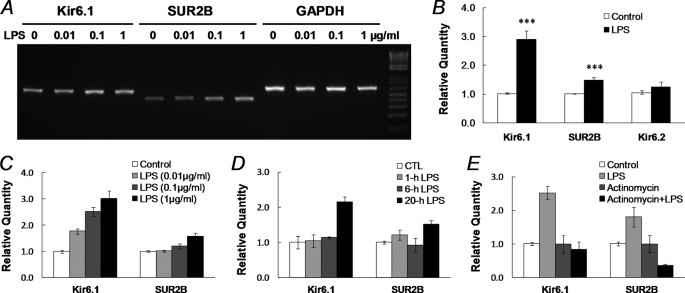
FIGURE 4.
Augmentation of KATP mRNA expression after LPS exposure. A, total RNAs were extracted from dissociated SMCs from the mouse aorta after 20 h of incubation with LPS in 0, 0.01, 0.1, and 1 μg/ml. In RT-PCR analysis, the LPS treatment led to up-regulation of both Kir6.1 and SUR2B transcripts in a concentration-dependent fashion. B, quantitative real-time PCR was performed to quantify KATP channel expression. Expression levels of target genes were normalized to the GAPDH mRNA level using the 2−ΔΔCt method (18). LPS (1 μg/ml, 20 h) increased Kir6.1 transcripts by ∼1.9-fold, and SU2B by ∼0.5-fold (***, p < 0.001, n = 48 and 50 samples from 14 mince, respectively), whereas Kir6.2 did not show significant increase (p > 0.05, n = 33). Note that the expression of the KATP channel in LPS-treated groups was measured and normalized to the vehicle control. C, concentration-dependent Kir6.1 and SUR2B expression following 20 h of LPS treatment. Data were collected from three independent experiments with 3–4 samples in each. D, time dependence. A clear up-regulation of Kir6.1 and SUR2B mRNA expression was observed with LPS (1 μg/ml) exposure at 20 h but not at 1 and 6 h. E, after a 20-h treatment with actinomycin D (2 μg/ml, added 1 h before 1 μg/ml LPS), the enhancement of Kir6.1 and SUR2B expression was totally eliminated. Data were obtained from three independent experiments with 3–4 samples in each.