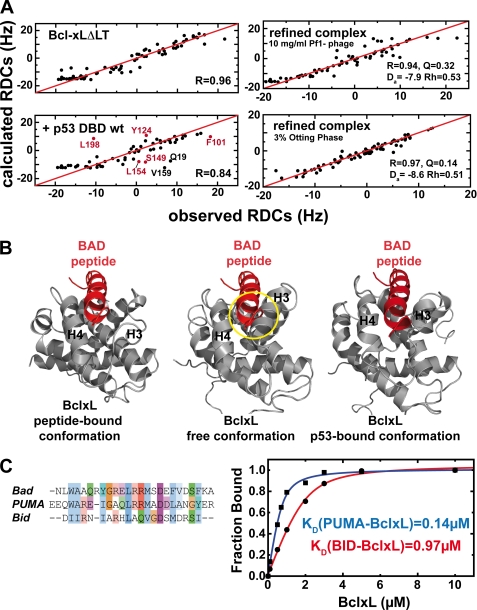
FIGURE 3.
Structural changes in BclxL upon binding to p53DBD monitored with residual dipolar couplings. A, comparison of the observed and calculated HN residual dipolar couplings of BclxLΔLT (upper left) and BclxLΔLT in the presence of wild-type p53DBD (lower left). Residues showing significant deviations in the BclxL-p53DBD sample are labeled and residues in the BH3-peptide binding site are colored in red. In the presence of wild-type p53DBD, the correlation between observed and back calculated RDCs is decreased from 0.96 to 0.84, indicating a structural change at the BH3 binding groove in BclxL upon complex formation. For back calculation of the RDCs a RDC-refined structure of free BclxL was used. Upper right, HN RDCs of BclxL in its complex with p53DBD (using 10 mg/ml of Pf1 phage for partial alignment) are correlated with HN RDCs back calculated from an RDC-refined structure of BclxL in complex with p53DBD (see B, right panel). The agreement between both sets is very high, yielding a correlation coefficient R of 0.94 (where R ranges from 0 to 1). Da, axial component; Rh, rhomicity of the alignment tensor obtained using single value decomposition with the refined structure of BclxL. Lower right, HN RDCs of the BclxL-p53DBD complex using 3% Otting phases for alignment. For back calculation an RDC-refined structure of BclxL in complex with p53DBD was used (B). Here, the calculated correlation is even better than found for the Pf1 phage case (r = 0.97). B, comparison between BclxL structures in the Bad-peptide bound form (left panel), in the free form (middle panel, PDB code 1lxl), and in the RDC-refined p53DBD-bound form (right panel). In the RDC-refined structure helices 3 and 4 move to a more open position similar to the conformation found when in complex with BH3 peptides and thus seem to facilitate peptide binding. In each structure, the BAD peptide is shown to visualize possible sterical clashes that can be seen in the free conformation of BclxL (yellow circle). C, left, alignment of BH3 peptides. Especially, Bad and Puma show high sequence conservation, whereas the similarity with Bid is less pronounced. Right, affinities between 0.75 μm fluorescein-labeled Puma and Bid BH3 peptides and BclxL measured in 10 mm sodium phosphate, pH 7.2, 1 mm DTT at room temperature.