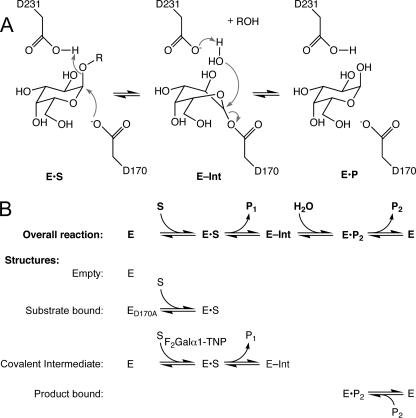
FIGURE 1.
α-GAL reaction and trapping stages for crystallographic analysis. A, double displacement reaction mechanism in human α-GAL. Asp-170 acts as the nucleophile, and Asp-231 acts as an acid and then a base over the course of the reaction cycle. B, structures of the different stages in the catalytic cycle. Empty enzyme (blue) required a cryoprotectant sterically excluded from the active site. The substrate-bound structure (green) resulted from deletion of the active site nucleophile, followed by addition of a disaccharide substrate. The covalent intermediate (yellow) used a difluoro-substituted galactoside to slow the second stage of the reaction. The product-bound structure (red) resulted from product inhibition of the enzyme. The color scheme is maintained throughout.