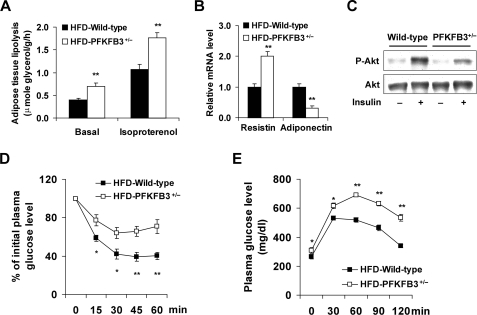
FIGURE 3.
Disruption of PFKFB3/iPFK2 exacerbates HFD-induced adipose tissue dysfunction and systemic insulin resistance. At the age of 5–6 weeks, PFKFB3+/− mice and wild-type littermates were fed an HFD for 12 weeks. For A, B, D, and E, data are means ± S.E., n = 6. *, p < 0.05 and **, p < 0.01 HFD-PFKFB3+/− versus HFD-wild-type. A, rates of adipose tissue lipolysis were measured under both basal and isoproterenol-stimulated conditions. B, changes in the mRNA levels of adipose tissue resistin and adiponectin. C, adipose tissue insulin signaling. After anesthesia by an intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of pentobarbital (50 mg/kg body weight), mice were injected with insulin (1 units/kg) or PBS into the inferior vena cava (i.v.) and epididymal adipose tissue samples were collected 5-min later. For D and E, mice were fasted for 4 h and received an intraperitoneal injection of insulin (1 units/kg) (D) or d-glucose (2 g/kg) (E).