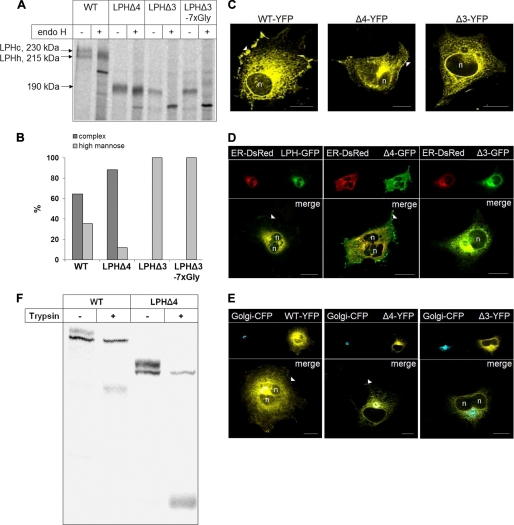
FIGURE 2.
Glycosylation pattern and subcellular distribution of LPH wild type (WT) and domain deletion mutants in COS-1 cells. A, transiently transfected COS-1 cells were biosynthetically labeled for 8 h with [35S]methionine followed by immunoprecipitation. The immunoprecipitates were divided into two aliquots and treated with endo H or not treated. The proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography. B, densitometric scanning of the endo H treated biosynthetic forms of wild type and mutant LPH shown in A. C, confocal analysis of transfected COS-1 cells. D and E, colocalization of LPH mutants with ER and Golgi markers, respectively, in transfected COS-1 cells. COS-1 cells were co-transfected with GFP-tagged LPH proteins and ER-DsRed- or YFP-tagged LPH proteins and galactosyl transferase-CFP, respectively. Confocal analysis with living cells was performed 48 h after transfection. n, nucleus; arrowheads, cell surface; bars, 20 μm. F, transiently transfected COS-1 cells were biosynthetically labeled for 4 h with [35S]methionine followed by treatment of the intact cells with 50 μg/ml in fetal calf serum-free Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium for 30 min at 37 °C. The reaction was stopped with cold fetal calf serum and protease inhibitors. Detergent extracts were immunoprecipitated with mAb anti-LPH and subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography.